
Chapter Outline
· What are emotions and Moods?
· Emotional Labor
· Effective Events Theory
· Emotional Intelligence
· OB Applications of Emotions and Moods
(Q. Differentiate Emotions from moods and list the basic emotions and moods)
There are three terms which are closely related with each other, first is Affect, second is Emotions and third is Moods.
Affect: it is a generic term, which covers long range of feelings including both emotions and moods.
Emotions: Emotions are intense feelings directed at something or someone.
Several studies have found that emotions are more short-term and fleeting than moods. if someone is angry, he will recover the reaction quickly. Emotions are show to people in different situations, when they are angry or happy or afraid of something.
Moods: these are less intense feelings in comparison with emotions and often rise without specific event acting as stimulus.
When someone is in the bad mood, he may feel bad for several hours.

The Basic Emotions:
There are so many emotions, which includes, sadness, pride, surprise, anger, enthusiasm, frustration, embarrassment, happiness, disappointment, disgust, embarrassment etc.
Rene Descartes (a founder of modern philosophy) presented six simple and primitive passions, which are, wonder, love, hatred, desire, joy and sadness. As per him, all other emotions are extended types or evolve from or species out of these six mega emotions.
Psychologists try to identify basic emotions through facial expressions, but there is a problem, the emotion that we Experience might not the way it appears. The meanings of emotions vary from culture to culture, For Example: in America and middle east smile on face is often the sign of happiness but in Middle East a smile is often taken as sexual attraction, so women avoid to look at men with smiley face.
Its very unlikely that philosophers and psychologists will ever agree on some specific set of universal emotions but still most of the researchers have shown their agreement for six essential universal emotions, which are: Anger, Fear Sadness, Happiness, Disgust and Surprise.
The Basic Moods: Positive and Negative Affect
Emotions can be positive or negative. Positive emotions express favorable feelings, such as and gratitude. Negative emotions show unfavorable feelings and evaluations, like, anger or guilt.
When we differentiate emotions into positive and negative, they become moods, because we now look at them more generally. These moods are further explained in the picture below.

Negative emotions often become negative moods. People recall events that created negative emotions five times than about the event which creates positive emotions. Why so, there is a concept Positivity Offset, it means at zero input, maximum people enjoy good mood that means positive mood, so we can say positive moods are quite common in routine lives, so, if anything bad happens, people feel it deep.
Cultural Differences: Research says Chinese people report fewer negative and positive emotions than people with other cultures. US culture considers enthusiasm as more productive, while Chinese people think negative emotions are more constructive. Pride is taken as positive emotion in western individualistic cultures (US citizens), while easter cultures like, Chinese and Japanese find pride as undesirable.
The Function of Emotions:
(Q. Discuss whether emotions are rational and what are their functions.)
Do Emotions make people irrational?
When someone becomes emotional, he or she is not rational anymore at that particular moment. The expression of emotions makes you brittle, weak and irrational.
Still, researches show that emotions are critical to rational thinking. Because emotions provide important information about how we understand the world around us. To make better decisions it is important to employ both thinking and feeling.
Do emotions make us Ethical?
Research is focusing on to examine the relationship between emotions and moral attitudes. This thing has raised questions on previous set of beliefs that decision making is highly cognitive in nature.
Sympathy for the suffering of others or guilt feeling on own misbehave with others are Examples of Moral Emotion.
Let’s take some other examples for better understanding; consider yourself, you heard a news of terrorist attack in school in Afghanistan, or when you heard the news of Christchurch Mosque Shooting in New Zealand, or when you heard that tsunami hits Japan in 2004 with the magnitude of 9.1, after hearing all these news what was your reaction, you went emotional or started cognitive calculations. Obviously, all of we felt bad for them and send our sympathize for them.
Conclusion: when people behave ethically, they at least partially make decisions based on feelings and emotions, and emotional reaction is often a good thing.
Sources of Emotions and Moods:
Following are the nine primary influences, let’s discuss each briefly.
Personality:
Some people are more emotionally sensitive, they have built-in tendency to experience certain emotions and moods. People feels same emotions with different intensities, termed as Effect Intensity.
People who are effectively intense, they feel both positive and negative emotions more deeply, when they are happy, they are really happy and when they are sad, they are really sad.
Day of the Week and Time of the Day:
Research says, people have bad or negative mood on Monday, show highly positive mood on weekends.
If we talk about the time, early morning in offices is often not the good time to ask for a favor or convey bad news and gradually when the day passes, at mid-morning people show good moods and start interacting with co-workers, etc. below mentioned picture shows the result of research about changing of people’ mood.

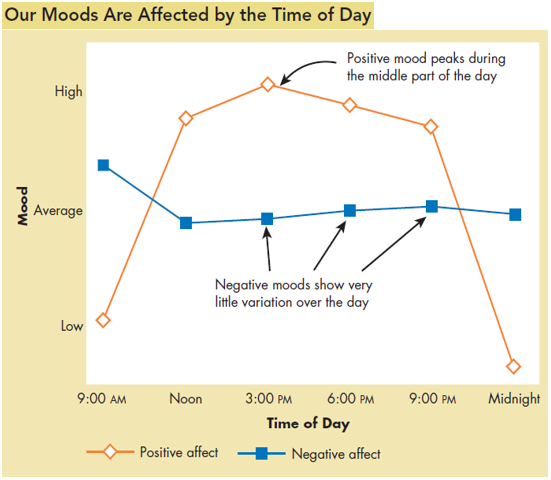
Weather:
People think they are in good mood in cold weather, rainy days, and don’t show positive moods in hot sunny days.
In fact, research says, this dependence of mood on weather is very little. There is phenomenon called as Illusory Correlation, it explains why people think they are in good mood in rainy days or in nice weather. It happens, when people start associating two events that in reality don’t have any connection.
Stress:
All of we would have experienced that, stressful days don’t have positive effect on moods and emotions. But still, research says, moods vary with person to person during stress hours. Some people like challenging task. Causes of stress may be challenging task (this may keep people in high spirits), repetition of same task, fatigue etc.
Social Activities:
Social activities too have positive effects on moods, now people’ mood depends upon what type of social activity they like the most. It may be hiking, walk with friends, travelling, parties, or even simple sitting and chit chat with friends can drive positive moods.
Two points are, whether good mood seeks social interaction or social interactions cause people to experience positive moods. Both the statements are correct.
Sleep:
Research shows, there is great impact of sleep on moods, adult-worker and under-graduates who can’t sleep well bad feeling of anger, fatigue and hostility, bad sleep also leads to poor decision making and difficult to control emotions. Poor sleep is also greatly associated with job satisfaction because people feel fatigued and irritable.
Exercise:
If you are in stress, start exercise, it will reduce your stress. Research consistently shows, exercise stimulate the positive moods, so, make it your habit. But don’t expect miracles.
Age:
We often believe that people experience positive emotions (so-called youthful exuberance), in fact this is the wrong belief.
Research shows that as people grow, they experience positive moods for longer time and negative moods fade quickly.
Sex:
It is a common perception that women are more emotional than men, and its true. It is observed that women tend to hold both positive and negative emotions for longer period of time, except anger. Evidence from 37 different countries shows that men pose higher level of powerful emotions like anger, and women show more powerless emotions like sadness and fear. So, we can say that there are sex differences in experience and expression of emotions.
People interpret differently while assessing moods and emotions of women and men, people detect angry expressions on males faces quickly and happy expressions on female faces. Neutral face of a man is attributed as more angry and neutral face of woman is seen as happy.
An employee’ expression of organizationally desired emotions (willingly or unwillingly) during interpersonal transactions at work.
This concept of emotional labor is emerged from study of services industry or service jobs.
Example: Sales staff is expected to greet customers with smile, flight attendants are expected to treat customers with smiley faces, doctors are expected to be neutral whether they want to be or not.
Emotional Dissonance: it is to project one emotion while feeling another, that means, when you are internally broken and at the same time you are supposed to greet customers with smile. It can lead to emotional exhaustion and burnout.
To understand it better, lets separate both emptions into felt and displayed ones,
· Felt Emotions are the actual emotions that the employees have.
· Displayed Emotions are those which are expected from employees on the job.
To display fake emotions requires us to suppress the real emotions,
· Surface Acting: it is related with displayed emotions; it is to hide real emotion and act the way it is required on the job.
· Deep acting: it is to modify the real emotions into the ones which are required on the job. It is related with felt emotions.
How emotions and moods influence our job performance and satisfaction is described in Affective Events Theory (AET).
It says that, employees react emotionally to things and events that happen to them during work, and this reaction influence their job performance and satisfaction.

As per this theory, emotions are a response to an event occurred in the work environment. Work environment includes degree of autonomy on job, number of tasks and their nature, job demands or requirement of emotional labor.
This environment creates work events like uplifting events (fulfilling job requirements, getting support from colleague, or receiving appreciation upon accomplishments) or hassle (employees if they refuse to complete their task in time, excessive time pressure, conflicting demands from different managers) or sometimes both.
These work events further produce positive or negative emotional reactions. People who score low on emotional stability will most probably react strongly to negative events and vice versa in case if employees score high on emotional stability.
So, emotions influence greatly a number of performance and satisfactions variables, which includes, organizational commitment, level of effort, workplace deviance, intentions to quit, organizational citizenship behavior.
Research and tests of this theory shows following results:
· Emotion-driven behaviors are mostly short in duration are highly variable.
· As emotions and moods fluctuate with time and so, their effect on performance also fluctuates.
· At any given time, current emotions greatly influence job satisfaction, along with the prior history of emotions surrounding the event.
· As emotions are not compatible with behaviors required to do a job, so, they typically have negative influence on job performance.
· An emotional episode is in-fact a series of emotional experiences, precipitated by a single event and containing elements of both emotions and mood cycles.
This AET provides us two important messages, First, Emotions provide important information about how workplace hassles and uplifting events influence employee performance and satisfaction, Second, managers and employees should not ignore even minor emotions and events that cause them because they accumulate.
“It is the ability to sense and manage emotional cues and information.”
It is the person’ response to perceive emotions in the self and in others, understanding the meaning of these emotions and then regulating one’ emotions accordingly in a cascading model.
People who understand their own emotions and have the ability to read the emotional cues, if you know that why you are angry and how to express yourself without violating the norms, is the most appropriate and effective way. Studies have show that, EI plays important role in job performance.

The Case in favor of EI:
Intuitive Appeal:
It is good to process social intelligence. Intuition suggests that the people who can sense emotions in others, have control on their own emotions and manage social interactions are mostly praised in the business world.
EI Predicts Criteria That Matters:
Research have shown that the high level of EI in a person means he will perform well on job. Evidence from different studies have shown positive relationship between EI and job performance.
EI is Biologically Based:
One study of a person with damaged brain shows that, he scored no lower on standard measures of intelligence than the person with no brain injury.
The Case Against EI:
EI Researchers Do Not Agree on definitions:
Many researchers are not clear about emotional intelligence, because researchers used different definitions. Some researchers use ability-based perspective on EI by conducting tests with right and wrong answers and then scoring the ability to recognize and control emotions.
Others described EI as a broad variety of constructs which can be measured by self-reports and are connected primarily in a way that they don’t have to do anything with cognitive intelligence.
Both of these definitions are different, even the perspectives used by researchers are also hardly related with each other.
EI Can’t be Measured:
Critics says, there is questions about measuring Emotional Intelligence, as it is a kind of intelligence. They say that there must be right and wrong answers for it on tests, though there are some tests which have right and wrong answers but the validity of some questions is doubtful.
EI is Nothing but Personality with a Different Label:
Some critics argue, as EI (especially emotional stability) is very closely related with Personality and intelligence, so there is nothing unique to offer.
Still, EI is more popular in consulting firms and it accounts for more than 85% of star performance in top leaders
Emotion Regulation:
Emotional regulation is to calm yourself when you are angry or cheer yourself when you are feeling down. It is to identify and modify the emotions you feel. It is a part of EI literature.
Strategies to regulate emotions are: positive thinking, or to think about pleasant things, suppressing negative thoughts, engage yourself in relaxation techniques or distract yourself.
Individuals’ ability varies in this emotional regulation, individuals with high personality traits, find themselves more difficult in regulating emotions as their moods are often beyond control and individuals with lower level of self-esteem find difficult to improve sad moods.
Selection:
Employers should consider EI factor while selecting a new employee, as it is observed in research that the employees hired on the basis of higher EI level performed far better than other employees.
Decision Making:
OB researchers have found that emotions and moods play important part in decision making. Positive emotions enhance problem solving skill and people with good moods or positive emotions are more likely to use rule of thumb or heuristics to help taking good decisions so quickly.
Another study suggested that, people with negative emotions or depressed are slower at processing information so this makes them poorer decision makers.
Creativity:
People with good mood are often more creative, flexible, allows themselves to think openly and produce more ideas than the people in bad moods. So, supervisors should try to keep their employees in good moods as this will make them more creative and beneficial for the organization.
Some researchers don’t agree with this relationship between positive emotions and creativity, they argue that good moods or positive emotions may make them feel relax and people avoid critical thinking.
Motivation:
Research have show that, employees with positive moods and emptions are more motivated than other employees. There runs a cycle, positive emotions and moods make people more creative, which leads to positive feedback from people observing them, this positive feedback will make employee’ mood more positive which in return will make employees to perform even better than before. And the cycle goes on.
Leadership:
Emotions play important role in leader’ effectiveness. Leader can energize subordinates, followers when he is excited, active and enthusiastic and convey a sense of competence, efficacy, enjoyment and enthusiasm.
Negotiation:
It is said that a skilled negotiator has a “Poker Face”, as negotiation is an emotional process. If you have got angry nature, then you need to use anger selectively, because better informed individuals are often less willing to share information or meet an angry opponent halfway. Emotions and moods have benefits at work, in negotiation.
Customer Service:
Employee’s emotions play important role in proving customer services. If employee is with good mood, he will provide best customer services, that will lead to repeat purchases, and in the end company’ sales will increase.
Employee’ emotions can be transferred to customers. If employee is in bad mood, he will make customers feel bad. This matching effect is Emotional Cognition. Catching emotions from others.
Job Attitudes:
We often heard the advice that “never take your work home”, but its not that much easy to act upon this advice.
If employee has spent good day at job, he will stay happy and will enter the home with happy emotions and mood, which in return will make the home environment pleasant and vice versa.
The emotion you take home will be transferred to your family.
Deviant Workplace Behaviors:
When we work in an organization, we observe that employees often violate the norms and act in a way which is against the norms of the organization. This is Deviant Workplace Behavior. This may be due to negative emotions or bad mood. Angry employee looks for someone to blame for their bad mood.
Safety and Injury at Work:
Negative moods cause distractions which lead to careless behavior. If an employee is in bad mood, there are more chances that he will get himself hurt.
For example, if an employee is scared, he will become more pessimist, because he feels that he will get hurt anyway, so while confronting such situation, he might get freeze or panic which will cause him hurt.
So, make sure, if an employee is in bad mood, keep him away from dangerous activities.
How Managers can Influence Moods:
Managers can bring humor while interacting with employees in bad mood, or appreciate them for their work, this will make them feel good.
If leaders are in good mood, his subordinates and colleagues will also experience pleasant environment, and they will become more cooperative.
Finally, selecting team members of positive attitude will affect team performance positively overall.