
Chapter Outline
· Attitudes
· Job Satisfaction
According to one definition: “Attitude is one’ behavior and the way of coping with the things he deals in the routine life.”
Attitudes are quite complex, if we ask someone about their attitude towards a celebrity, or organization he works in, or religion, his answer would might be simple, but the underlying reasons are often complicated.
Example: when someone says, “I don’t like my job”, he is expressing his attitude towards job.
What are the main components of Attitudes?
There are three components of attitudes, these are cognition, effect and behavior.
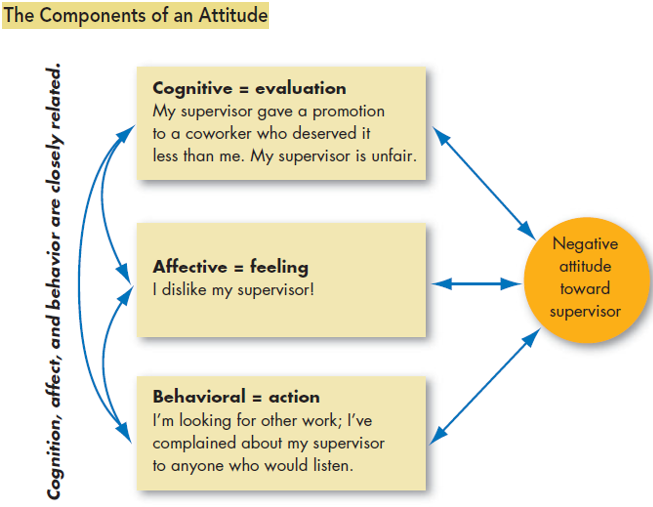
Cognitive Component: when someone says, I am not satisfied with my salary, this actual reality is the cognitive component. Which sets the base for next component.
Affective Component: this reflects emotions and feelings, like, I am very upset, my salary is low.
Behavioral Component: then comes the last component, it is the show of behavior, how employee will behave in a certain way, it can be kind of “as I am upset due to my low pay, so I am looking for a new job”
These three helps greatly in understanding attitudes, the relationship between attitudes and behavior, cognitive and effective components are often inseparable in many situations.
Does Behavior Always Follow from Attitudes?
(What is the relationship b/w attitudes and behavior?)
Attitudes of people determines what are they up to or what they do, common sense also supports this relationship.
Example: we visit places we like, or we watch tv shows we like.
But in late 1960s, Leon Festinger challenged this effect of attitude on behavior. He argued that attitudes follow behavior. Example, people often change what they say to match it with what they do.
Leon described this attitude following behavior as Cognitive Dissonance, the mental discomfort that results from holding two or more conflicting attitudes or between behavior and attitudes.
Evidences have shown that, people want to bring consistency in their attitudes and between their attitudes and behavior to minimize the dissonance but, no individual can fully avoid dissonance.
Festinger proposed two moderating factors to reduce dissonance, which are importance of elements creating dissonance and how much influence we believe we have over them, and the third factor is reward. If the rewards are high with the high dissonance, this will reduce the tension inherent in the dissonance.
Moderating Variables
There are five powerful most moderators of attitudes relationship are
· Importance of attitude: these attitudes show strong relationship with behavior and reflect fundamental values, self-interest and identification with individuals or groups.
· Correspondence to behavior: specific attitudes predict specific behaviors and general attitudes best predict general behaviors.
· Presence of social pressures: differences occur between attitudes and behavior is often due to social pressure to behave in a certain way.
· Its accessibility: kind of attitudes which memory can quickly access and recognize are more likely will predict person’ behavior. We remember such attitudes which we express frequently.
· Direct experience with attitude: the relationship between attitude and behavior will be stronger when attitude is subject to some specific incident with which we have direct personal experience.
What are the Major Job Attitudes?
OB researchers have found three major job-related attitudes which employees hold are: Job satisfaction, job involvement and organizational commitment. Some other important attitudes are perceived organizational support and employee engagement. Let’ see each of these attitudes in little detail.
Job satisfaction:
Employee attitude refers towards job satisfaction, these are the feelings of employee about their job. If a person has high job satisfaction, it means he holds positive feelings about the job. Vice versa in case of person with low job satisfaction.
Job Involvement:
Job involvement is related with job satisfaction. It is what a person identifies with his job, participates in it and considers performance important to self-worth.
Employees who are with high level of job involvement really care about the job characteristics and the kind of work they do.
There is another closely related concept, that is Psychological Empowerment, these are the employees’ beliefs, to which degree they effect their work environment, the meaningfulness of their job, their competence and perceived autonomy in their work.
Higher the level of job involvement and psychological empowerment are positively related with job performance and organizational citizenship. It is also greatly related with reduced absentees and lower resignation rates.
Organizational Commitment:
When employee show his commitment with organization and its goals and want to remain its member for long, it’s Organizational Commitment. Emotions and beliefs in its values are considered as “gold standard” for employee commitment.
Researches have shown positive relationship between organizational commitment and job productivity. When employees are committed then they continue to work whether if they like it or not and they make sacrifices for organization.
If organizations fail to fulfil their promises, then employees become less committed and it leads to lower productivity and it results in absenteeism and turnover
Perceived Organizational Support:
It is the belief of employees that, organizations will support them in the times of need. Higher the POS (Perceived Organizational Support) higher the organizational commitment, higher organizational citizenship behavior, better customer services and lower levels of tardiness.
Employee Engagement:
It is employee’ involvement, level of satisfaction and enthusiasm for the work he does. Do the employees have access to organization’ resources, whether they feel their work as meaningful and important, given opportunities to learn new skills and whether their interactions with supervisors and co-workers are rewarding.
Higher the employee engagement higher the passion for work and disengaged employee often put time in work with no energy.
Are these job attitudes Really All that Distinct?
Researches have suggested that the above-mentioned attitudes are highly related with each other. For example, the relationship between perceived commitment support and organizational commitment is very strong.
Measuring Job Satisfaction:
The positive feelings about a job after evaluating job’s characteristics.
Job is not just about completing the required tasks, on job employees need to interact with co-workers and supervisors, meeting performance standards, obey rules, etc. All these factors play important role in measuring job satisfaction.
There are two approaches to measure job satisfaction, these are,
First is, asking a single question “keeping all factors in mind, how satisfied you are with your job”, respondents ae given rating scale ranging between 1 to 5 from highly satisfied to highly dissatisfied. And respondents rate the job on the scale accordingly.
Second is, identifying key job factors like interaction, rules, pay, environment etc., respondents rate each factor, and in the end, researchers add the rating to get overall job satisfaction score.

How Satisfied are People in their Jobs?
The answers to this question are mix. Depending upon the job characteristics, organizational environment, rules and regulation, cultural differences, employee’ personal nature and temperament of doing job, etc.


What Causes Job Satisfaction?
Factors that cause job satisfaction varies from employee to employee, but most of the employees like the job if there are trainings, variety, control, independence, Interdependence of shared tasks, feedback, interaction with coworkers, social support.
Job satisfaction is not just about the job conditions. Employee’ own personality also plays important part in job satisfaction. People with positive core self-evaluation, people who believe in their inner worth and basic competence (they like challenging tasks) are more satisfied with their jobs than people with negative core self-evaluation. Due to this negative attitude toward learning, these people often got stuck in boring jobs.
The Impact of Satisfied and Dissatisfied Employees on the Workplace:
Researchers have developed a theoretical model; it illustrates four responses (exit-voice-loyalty-neglect) which differ along two dimensions (constructive/destructive and active/passive)
· Exit: It shows the behavior of employee towards leaving the organization, it also includes, looking for a new position as well as resigning.
· Voice: this response includes actively participation of employee to improve conditions, it also includes suggestions for improvement, discussing with supervisors on some problem and taking part in unions.
· Loyalty: this response comes, when employee is so loyal with the organization, he stands for the organization against criticism, wait for the conditions to improve and trusts the management that they will do the right.
· Neglect: this is the negative response, includes absenteeism, increase error rate, reduced effort and let the conditions to go worse.

Exit & Neglect: response revolve around the performance variables like effort, productivity, turnover, absenteeism.
Voice & Loyalty: lets the employees to tolerate the unpleasant situations or to reinstate satisfactory working conditions.
Job Satisfaction and Job Performance:
Results of 300 studies have found that if employees are satisfied then they are more productive. If employees are satisfied then they put extra effort in the job.
Job Satisfaction and OCB (Organizational Citizenship Behavior):
It is very logical that, if an employee is satisfied with his job, he will speak positively about his organization, will help co-workers and put more effort in the job. So, such evidences have suggested that, job satisfaction is moderately corelated with OCB.
Job Satisfaction and Customer Satisfaction:
In services industry, organization have to keep strong relationships with customers, and managers of such organizations know this reality. Organizations keep employees satisfied so in return they keep their customers happy and satisfied through better customer services.
Job Satisfaction and Absenteeism:
Studies have found that there is inverse relationship between employee satisfaction and absenteeism. If employees are satisfied then they don’t run from work.
There is one more point to note, that satisfied employees also take day offs if organizations allow them to take leaves when they need and when work load is manageable.
Employees with lower job satisfaction take more absents from the job and don’t put much effort in the job.
Job Satisfaction and Turnover:
If employees are happy with the organizations and satisfied with there work then they don’t leave the organization unless they get much better offer from some other job.
If employees are highly educated then there are more chances that employee will not stay in the organization, because he will be getting better options in the industry.
Job Satisfaction and Workplace Deviance:
When employees are dissatisfied then they break rules, join unions, spread propaganda, steal at work and tardiness etc. in order to control this workplace deviance, managers need to identify the root cause and try to solve the problem.
Managers often “Don’t Get it”:
Despite the importance of term “job satisfaction”, managers don’t take it seriously and ignore the signs of dissatisfaction and don’t take any action. They often overestimate while assuming that employees are satisfied or not, they assume most of the employees are satisfied, which is often not the case.
In one study of 262 organizations, 86 percent of employers believe that they treat their employees well but only 55 percent of employees agreed.