
Chapter Outline
· The importance of Interpersonal Skills.
· What managers do.
· Enter Organizational Behavior.
· Complementing Intuition with Systematic Study.
· Disciplines that Contribute to the OB Field.
· There are few Absolutes in OB.
· Challenges and Opportunities for OB.
Earlier the focus of business study was on studying economics, finance and quantitative techniques but later researchers found that studying human behavior is also equally important.
Managers with leadership qualities and communication skills made remarkable achievements in their careers.
Companies like Starbucks, Marriott, Cisco, Adobe systems etc. spend a lot on employee’s communication skills and human behavior.
Surveys showed that social relationships among co-workers and supervisors were strongly related to overall job satisfaction and lower intentions to quit.
Companies with good reputation and pleasant work place appears to make good economic and financial performance.
In today’s competitive and demanding workplace, managers cannot succeed on their technical skills alone but they also have to have good people skills.
Managers:
Managers complete tasks by involving other people in it. They allocate resources, define other’ tasks and make decisions to achieve goals. Managers oversee the activities of others who are responsible in attaining goals.
Managers perform their work in Organizations.
Organizations are consciously coordinated social units, in which two or more people work together on relatively regular basis for a set purpose.
Management functions:
Earlier in twentieth century an industrialist Henri Fayol presented five management functions, which were Planning, Organizing, Commanding, Coordinating and Controlling.
And now we have four management functions i.e., Planning, Organizing, Leading and Controlling.
Planning:
It is to define organizational goals, making strategy to achieve those goals and developing set of plans to integrate and coordinate activities. Planning takes place at mid or upper level of management.
Organizing:
When managers design an organization’ structure, this function is called as Organizing. It includes determining tasks, who will do these tasks, tasks grouping, who will report to whom and where decisions will be made.
Leading:
Every organization have people to work in. it is management’ job to direct and coordinate those people. This function is called as Leading. It includes motivating employees, direct them about their activities, resolve conflict among employees and select the most effective communication channel, etc.
Controlling:
Controlling is to monitor tasks as if the things are going as they were planned, comparing tasks with the previously set goals and if there is any deviation then correct them and put them back on track.
Management Roles:
Mintzberg concluded that managers preform ten different highly interrelated roles or set of behaviors, these are Interpersonal, Informational and decisional roles.
Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles:

Management Skills:
Researchers have found three types of skills managers need to achieve their goals.
Technical Skills:
Its about having knowledge or expertise. It means having technical knowledge of any field chosen. That means if a person is a doctor, he would be specialized in it. If a person is an engineer, he should be an expert of relevant engineering field. Etc.
Human Skills:
Its about communicating, supporting, understanding or to motivate individuals or groups. Some people are technically proficient but cannot communicate properly with team members or subordinates, cannot understand their problems etc., as managers gets job done through others so they should be in good terms with others.
Conceptual Skills:
Manager’s responsibility is to take decisions and analyze different situations, so for this they need to have conceptual skills. For example, how to integrate a new idea with the existing one, this requires having conceptual knowledge about it.
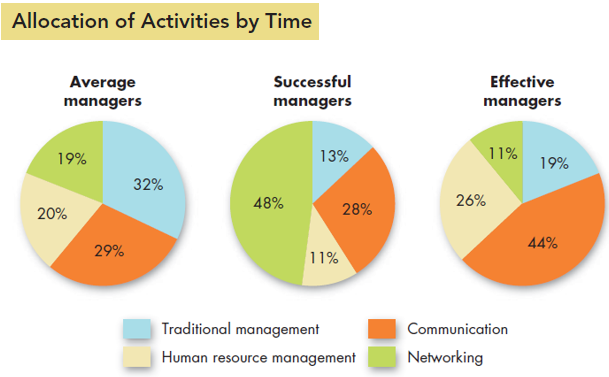
Effective Versus Successful Managerial activities:
Do all the managers work in the same way, so the successful managers were doing the same things as the less successful managers. Fred Luthans studied more than 450 managers to find the answers. All the managers were involved in four managerial activities. Those were:
Traditional management: Decision making, planning controlling.
Communication: Exchanging routine information and paperwork etc.
Human Resource Management: Motivating, managing conflicts, training, staffing, disciplining etc.
Networking: Socializing, politicking and interacting with outsiders.
A review of Manager’ Job:
Every single thread, whether it’s management functions, skills, activities or approaches have its own importance. There is not a single aspect to ignore if managers want to be effective.
Definition:
OB is the study of what people do in an organization and how their behavior effects the organization’s performance.
It involves studying three behaviors in organizations, which are individuals, groups and structures. As it is related with employment related concerns so it focuses on jobs, absenteeism’s, turnover, productivity human performance and management.
OB covers the topics like leader behavior, motivation, power, work design, conflicts, stress, attitude developments etc.
We are students of Behavior. We notice other’ behavior in different situations. Casual or common-sense approach of analyzing other can result in wrong predictions. But we can improve our predictive ability by adding intuition with a more systematic approach.
Systematic Study:
Looking at relationships, attempting to attribute causes and effects, and drawing conclusions based on scientific evidence.
EBM (Evidence Based Management):
The basing of managerial decisions on the best available scientific evidence.
Intuition:
A gut feeling not necessarily supported by research.
Relying too much on intuition often go worse. For example, as per a survey 86 % of managers thought their organization was treating their employees well, but only 55 % of the employees thought so.
So, use systematic study and EBM along with intuition while making important decisions
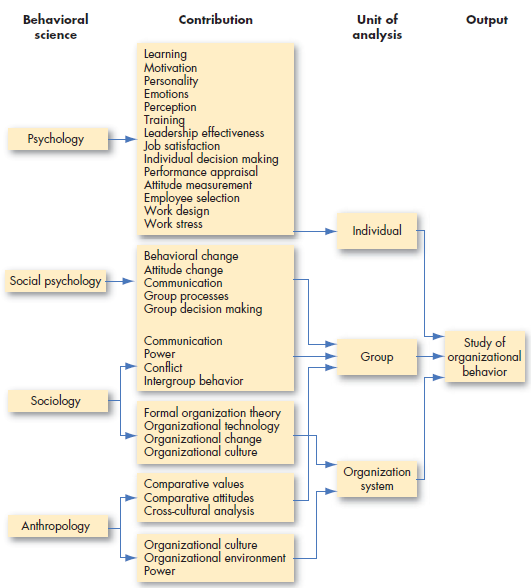
Psychology:
“It is to measure, explain and sometimes change the behavior of humans and other animals.”
Those who contributed and add knowledge to OB are personality theorists, learning theorists, counseling psychologists, industrial/organizational psychologists.
Earlier organizational psychologists focused on the problems like boredom, fatigue and other working conditions but now studies getting put their more focus on factors like perception, personality, emotions, motivational forces, decision making process, performance appraisals, job design, job stress, attitudes etc.
Social Psychology:
It is considered as a branch of Psychology and in fact it is a mixture of concepts from both psychology and sociology.
It focusses on the individual’ influence on each other, and the study of change, how to implement it and eliminating or reducing hindrances in its acceptance.
Social psychologists also contributed to measuring, understanding and changing attitudes i.e., identifying communication patten and building trusts. And the study of group behavior, power and conflict.
Sociology:
Sociology studies the people’ relationship to their social environment and culture. In OB it focusses on group behavior in organizations specially in formal and complex organizations.
Sociologists focused on studying organizational culture, communications, power, conflict, formal organization, organization theory.
Anthropology:
It is the study of societies to learn about human beings and their activities.
Anthropologists work on cultures and environments, which help to understand differences in the fundamental values, attitudes and behavior between people in different countries and within the organizations.
Absolutes in OB are not as consistent as the principles and laws of physics, chemistry or astronomy. Human beings are complex. Two people act very differently in same situation or the same person’ behavior varies in different situations.
But Organizational behavior researcher’s concepts reflect situations or contingency and conditions. That means e.g., “x” leads to “y” under “z” conditions. These are Contingency variables.
In the past understanding Organizational behavior was never so important for managers. But now time is changing. New employment trends like contractual jobs or downsizing are making employees more insecure.
The typical employees are getting older and women and people from different cultures are working together. So, to cope with this, managers need to follow some basic OB concepts which are as follows:
Responding to Economic Pressures:
Managing employees in all the situations whether the time is bad or good is hard. OB suggests to reward, satisfy and retain employees in good times. In bad times, companies should focus on employee’ issues like stress, coping and decision making.
During difficult economic times, like in recession, the difference between good and bad management can be difference between profit and loss, even survival and failure.
Responding to Globalization:
The world has become a global village now and manager’ job is changed.
For example, Nokia, a Finland based mobile phone company recruit employees from India, China or from other developing countries, the situation is now that non-Finns have outnumbered the Finns at Nokia’ renowned research Center in Helsinki (capital of Finland).
And automobile companies like Ford (American based company) manufacturing in Brazil, Volkswagen (German firm) in Mexico, Mercedes (German Firm) and BMW (German Firm) in South Africa.
· Increased Foreign Assignments:
Managers in multinational firms are often sent to foreign operating divisions or subsidiary in another country. There they have to manage workforce with different needs, attitudes and aspirations from those they were used to back home.
· Working with people from different cultures:
In organizations where we work, we have to work with our colleagues, and bosses from different cultural backgrounds. What motivates me may not motivate my colleague.
So, to better manage this diversity, management practices need to be designed to reflect the values of different countries and cultures in which an organization operates.
· Overseeing movement of jobs to countries with low-cost labor:
Many organizations have headquarters in developed country and manufacturing facility in developing country. It’s simply because of availability of cheap labor.
In this way companies get the cost advantage over its competitors but local talent suffers in this case.
Managing workforce diversity:
Workforce diversity comprises of women and men, individuals with a variety of physical or psychological abilities, many ethnic and racial groups, and people who differ in age and sexual orientation.
OB will help to know how managers can use differences within groups as competitive advantage. what are legal requirements in each country, or does diversity even matters? Etc.
Improving Customer Service:
In today’ world, majority of people in the country work in service sector. i.e., 80% people in US, 73% in Australia, 69% in UK, 68% in Germany and 65% in Japan.
Service jobs include technical support representatives, sales officers, credit representatives, flight attendants, financial planners, waiters, etc. common characteristic of this job is interaction with customers. Train these employees enough so that they can answer all the questions asked by customers and provide them best solution for their problems.
Many companies fail because they could not provide better customer services, and as a result they lose customers and so had to wind-up.
Improving People Skills:
It includes, managers should be capable enough to understand the people at work.
OB will tell how to design motivating jobs, how to create effective team, techniques for improving your listening skills.
Stimulating Innovation and change:
Organizations should be open enough to accept change and bring innovation.
Organizations who don’t adopt change and innovate their services, products or procedures of doing business becomes extinctions.
So, companies should adopt change and bring innovation to attract customers and remain in the competition.
Coping with Temporariness:
Companies need to go fast and flexible to compete and survive in today’ world. So, they have to adapt adopt strategies like globalization, expansion or technological changes.
Temporariness refers towards strategy for current season, for specific customer, for running project, in the current market scenario, little technological changes, even varying working hours, temporary employees etc.
Managers should be skilled and trained enough to cope with this temporariness, flexibility. Spontaneity and unpredictability.
Working in Networked Organizations:
Networked organizations enable employees to communicate and participate from around the world.
In this type of organization manager’ job is so challenging, as it is difficult to motivate and lead people or employees sitting in other cities or countries than managing employees physically present in the organization. OB will guide manager, what skill they should develop to manage the work in this situation.
Helping Employees Balance Work-Life Conflicts:
Nine to five jobs are now the talk of gone days. Time has changed now. Priorities of both employees and companies are changing.
Employees are now complaining that the line between work time and non-work time is getting blurred. Researchers have found four reasons behind this conflict, are,
Firstly, the creation of Global organizations means, World never sleeps.
Second, communication technology allows many professionals and technical employees to work anywhere from world.
Third, organizations are asking employees to spare more time for job.
Finally, the rise of dial-career couple makes it difficult for marriage employees to fulfil commitments to home.
The following image will greatly help you to understand this conflict.

OB suggests managers how to design the job that may help employees to deal with work-life conflicts.
Creating a positive Work Environment:
Organizations are now taking positive work environment as competitive advantage.
OB researchers are focusing on positive work scholarship (Positive work environment), which studies, how organizations are developing human strength, vitality, resilience and unlocking potential.
OB also focusses on what’s wrong with organizations and its employees, what’s good about them. Researchers have found positive variables are engagement, optimism, hope and resilience.
Positive organizational scholars have studied a concept “reflected best-self”, means best thing or expertise of employee, ignoring the deficiencies and limitations. Focus on “what employees are good at, and exploit their strengths.”
Improving Ethical Behavior:
In today’ world full of tough competition, stress and expectation of increasing productivity, employees often opt to break rules, adopt unethical practices and engage in questionable practices.
Employees often face in daily routine ethical dilemmas, in which they have to make choices between right and wrong.
In global economy, where culture vary from country to country, it is difficult to determine, what is ethically right and wrong.
Managers in different organizations are spreading awareness in different ways i.e., writing and distributing codes of conducts, offering seminars, workshops and training programs to improve ethical behavior. Most importantly, managers are creating protection mechanisms to protect the employee who reveal the internal unethical practice.