
Chapter Outline
- What is HRM:
- The Trends Shaping HRM:
- Today’s new HRM:
- The New Human Resource Manager:
To understand HRM it is important to understand what managers do. An organization consists of people from different mindset, qualification and cultural backgrounds. These people have different duties to perform in the given time, all these people work together to achieve organization’ goal.
A Manager is responsible for accomplishing organization’ goals, managers do it by managing the efforts of people working in the organization. Researchers agreed upon, managing involves five basic functions, which are, planning, organization, staffing, leading and controlling. These five functions represent Management Process. Let’s briefly go through this process;
· Planning: It is to establish goals and standards; developing rules and procedures, developing plans and forecasts.
· Organizing: Assigning every subordinate, a specific task, establishing departments, delegating authority to subordinates, establishing chain of command and communication, coordinating the work of subordinates.
· Staffing: It is to determine what type of people company should hire, recruiting prospective employees, selecting employees, evaluating performance, training and developing employees, and counseling employees.
· Leading: getting people to get the job done, motivating subordinates and maintaining their morale.
· Controlling: It is to standards like, sales quotas, quality standards, product levels, carefully observing how actual performance compares with these standards and taking corrective measures where needed.
In HRM we will focus on staffing function i.e., personal agreement or human resource function.
HRM Definition:
“It is the process of acquiring, training, appraising and compensating employees and attending to their labor relations, health and safety and fairness concerns.” HR manager need to perform certain tasks, which include;
Manager’ Duties:
· To conduct job analysis (determining the nature of each employee’s job).
· Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates.
· Selecting job candidates.
· Orienting and training new employees.
· Managing wages and salaries (compensating employees).
· Providing incentives and benefits.
· Appraising performance.
· Communicating (interviewing, counseling, disciplining).
· Training employees, and developing managers.
· Building employee relations and engagement.
And what managers need to know about;
· Equal opportunity and affirmative action.
· Employee health and safety.
· Handling grievances and labor relations.
Why is HRM Important to all Managers:
HRM is important to all managers for several reasons, which are as follows;
Avoid Personnel Mistakes:
Studying HR is important to avoid personal mistakes. Following are some examples; managers don’t want to;
· Hire wrong employee.
· Experience high turnover.
· Having such employees which are not giving their best.
· Have your company in court due to your discriminatory actions.
· Have your company caught with unsafe practices.
· Have untrained employees, who is affecting department’ effectiveness.
· Commit any unfair labor practices.
Improving Profits and Performance:
It helps managers in understanding the most important thing that is, “you get results – through people”. The bottom- of managing is “getting results”. By studying HRM managers become able to manager their teams, develop better human resource for company, which eventually will increase company profits and performance.
Most of managers make perfect plans, layout clear organization charts, up-to-date technology and use modern accounting software but still fails, it is because they hired wrong people.
O the other hand, other managers succeed without adequate plans and other organizational controls, they were successful because they had the knack for hiring the right people for the right job.
You may spend some time as HR manager:
Managers may need to spend time in HR department to understand human needs, wants or preferences, their attitudes and values, motivation and satisfaction levels etc. most companies’ CEOs have once worked in HR department to make better decision. HR certifications are,
SPHR (Senior Professional in Human Resources),
PHR (Professional in Human Resources)
SHRM (Society for Human Resource Management)
HR for small businesses:
It is important to learn HR, as you may have to serve as your own HR manager. There are hundreds of thousands small business and many more registering every year. Most of new graduates will work for small businesses or will create new small businesses. As there is no need of proper HR manager in small businesses, so, owner himself or his manager do all the HR tasks.
Line and Staff aspects of HRM:
Authority is the right to make decisions, to direct the work of others and to give orders.
Line authority:
· It is when someone have authority to issue orders to other managers or employees.
· It is exercising authority within department.
· Example: When senior manager from marketing department orders assistant manager to prepare sales reports withing giving time.
· Managers exercising line authority are Line managers.
Staff authority:
· It is when someone have the right to advise other managers or employees.
· It is to manage all the departments.
· It is not an ordering relationship, its advisory relationship.
· Example: HR managers advises plant manager to use a particular selection test.
· Managers using staff authority are called as Staff managers.
Line Managers’ HRM Responsibility:
Line managers also perform many human resource duties. It is because, from president down to first-line supervisors – handling people have always been part of every line-manager. Line manager’ HR duties involve;
· Putting right person at right job.
· Orientation of new employees in the organization.
· Training new employees.
· Helping them in improving their performance.
· To gain creative cooperation and developing healthy working relationship.
· Interpreting company policies and procedures.
· Controlling labor costs.
· To develop the abilities of every employee.
· Creating and developing departmental morale.
· To protect employees’ health and physical conditions.
The Human Resource Department:
In small companies, line mangers perform all these personnel duties, they don’t need assistance. But as the organization grows, managers need assistance, specialized knowledge and advice of separate human resource staff. As shown in the picture below;
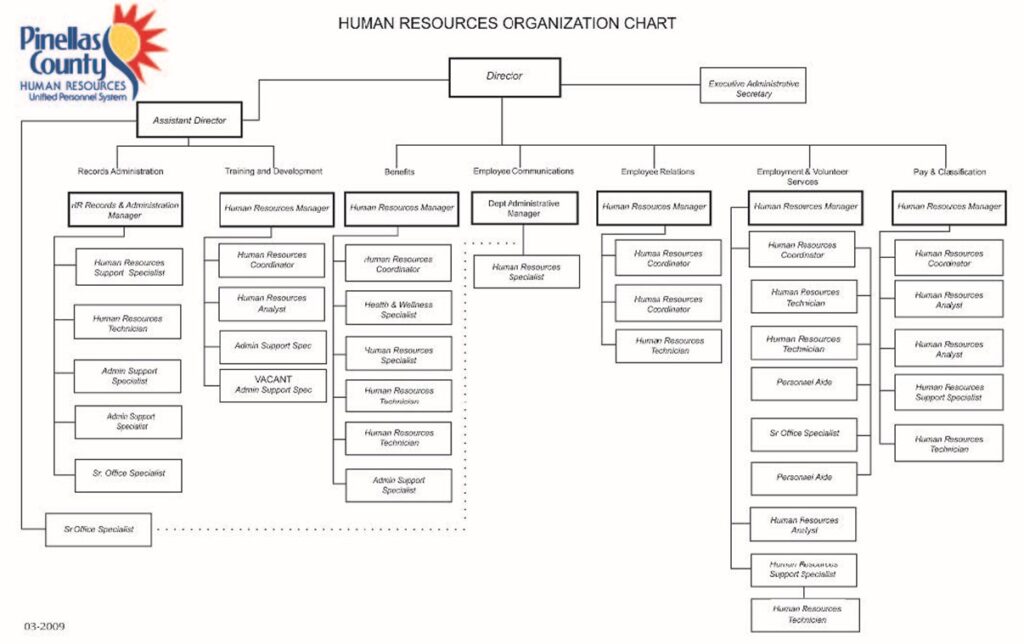
Some common positions in big organizations include; compensation and benefits managers, employment and recruiting supervisors, employee relations executive, training specialist, etc. some job duties include;
· Recruiters: They keep good terms within the community, travel extensively to search for qualified job applicants.
· Equal Employment Opportunity: They thoroughly monitor organizational activities for potential violations and compile and submit EEO reports.
· Job Analysts: Collect and examine detailed job duties to prepare job descriptions.
· Compensation Managers: Design compensation plans and handle employee benefit programs.
· Training Specialists: Plan, organize and direct training activities.
· Labor Relations Specialists: Advice management on all aspects of union-management relations.
New Approaches to Organizing HR:
With the rapid change in technology and techniques, what HR managers do and how they do it is also changing. Many employers are now thinking, how to improve HR functions. These may include;
· Shared services. (These are established HR units, their employees are shared with all companies, they interact through internet or calls, provide suggestions, support in day-to-day activities.)
· Corporate HR teams. (Helps top management in developing log-term strategic plans regarding personnel aspects.)
· Embedded HR teams. (Dedicating HR specialist to specific departments like sales or marketing department, to assist them in HR activities.)
· Centers of expertise. (Specialized HR consulting firms within the organizations. For example, to bring change in certain departments)
Trends occurring in the environment of HRM, which are changing how employers get human resource management tasks get done. Let’s have a look at these occurring trends;
Workforce demographics and diversity trends:
The composition of workforce has always been changing and will continue to change in coming years too. It will become more diverse in coming times, with more women, minority groups and older workers in the field. Below mentioned picture presents a bird-eye view of US workforce.
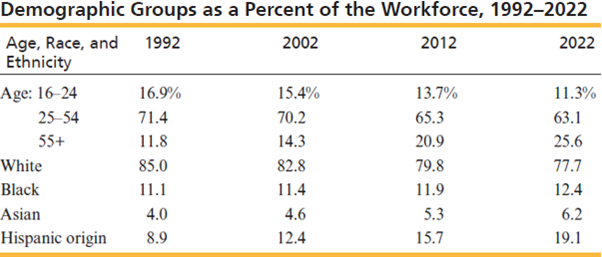
As it is seen in the figure, young employees are continuously falling and aging workforce is increasing. It is a big problem. So, US have to hire skilled foreign professionals. As per an estimate US bring around 181,000 foreign workers every year.
Trends in how people work:
Talking about US and Europe, jobs are shifting from manufacturing to service jobs. Over two-third of US workforce is employed in producing and delivering services, not products.
On-Demand-workers:
These are employees which aren’t employees
at all. For example, people who register themselves with Uber, or Airbnb type
of companies. They know they are not permanent employees; they are called for
their services when needed or on-demand.
One critic says, these types of jobs are
unpredictable and highly insecure.
An article in New York Times says; the larger worry about on-demand jobs is not about benefits, but lack of agency, a future in which computers, rather than humans determine, what you do, when and for how much. Some Uber drivers have sued the company to become regular or permanent employees.
Human Capital:
It is the workers’ knowledge, education,
training, skills and expertise. In todays fast growing world employers are
highly interested in enhancing “Human Capital”. Employees need to improve
education and knowledge on regular basis both in service and manufacturing sector
jobs. Some job examples are layers, bank tellers, retail clerks, bill
collectors, IT professionals, field engineers, etc. Every job needs
advancement.
Globalization trends:
It refers towards, companies extending their operations to new markets abroad. Companies are now selling worldwide and setting up assembling or manufacturing units abroad. Example Apple assembles iPhone in China and India.
Globalization has gain boom from around last 50 years. Example: US has increased imports and exports from $47 billion in 1960 to $562 in 1980 to about $5.1 trillion recently.
Free trade areas and agreements, reduced tariffs and barriers and such arrangements like NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) and EU (European Union) also encouraged international trade.
To go global companies, need to hire employees in other countries. Obviously, employees from different regions carries different traits, customs, religions or attitudes. Managing this “People” aspect of globalization is a big task for any company and its HR manager.
Economic trends:
Globalization supported growing global economy. Between 2001 to 2007 GDP (Gross Domestic Product) boomed, during this period home prices increased around 20% per year and unemployment remained controlled at about 4.7%.
The period from 2007 to 2015 was difficult economically. Economy collapsed between 2007-2008, and GDP fell. Home prices dropped by 10% and unemployment rose to 10%. It all happened because, the previous boom was made on debt. Banks freely lent loans to consumers. People spent for almost 20 years more than they earned. With fewer regulations, many businesses and consumers were soon deeply in debt. Consumers now stopped buying and economy tanked.
Economy then started recovering, and unemployment rate decreased to around 5% in 2015, and to 4% in 2018. GDP was growing at about 4% in 2018.
Worker Demand: almost half of employed US college graduates are doing odd jobs, that generally requires less than a four-year degree college education. Most of the jobs that economy added, did not required college education.
Skills Gap: about two third of occupation do not require post-secondary education for entry. These imbalances are complicated by a skills gap.
Unemployment: in some hi-tech occupations, like engineering, medical doctors etc., unemployment rates are low, while in others unemployment rates are still very high. Many people are working today in jobs below their expertise. This results in, around 70% of employees are found psychologically disengaged at work.
The bottom-line is, there is growing
pressure on employers to get the best efforts from their employees.
Technology trends:
Technology plays major role in shaping human resource management today. For Example: many companies use to connect with new recruits via LinkedIn, it often let line managers to bypass the human resource management unit.
Five Types of Digital Technologies: following are five digital technologies which are playing role in transferring functionalities from HR professionals to automation. These are:
· Social Media: It is affecting in such a way that, employers use tools such as LinkedIn, Twitter or Facebook rather to recruit new employees, rather than giving task to employment agencies.
· Mobile Applications: Companies use mobile applications to track or monitor their employees at work. It may be used to get live location, or digital photos at facility.
· Gaming: using smart and games to give training to employees or objective setting. Employees learn and complete tasks in fun way. In return they get appraisals etc.
· Cloud computing: these are intuitive user interfaces, which provides reports to employers on different things like, teams goal attainment progress and providing real time evaluative feedback.
· Data
analytics: it is to use
algorithms or statistical tools and problem solving to identify the
relationships among data for the purpose of solving particular problem. If we
apply it to human resource management, data analytics is called as Talent
Analytics. Example: It can help in understanding what are ideal
candidate’ traits etc. or can tell in advance which of the best candidate is
likely to quit.
A Brief History of Personnel/Human Resource
Management:
Personal management is not new, in ancient times, the tasks, like, attracting, selecting, training and motivating employees were the part of every manager’ job.
In late1800s, labor problems began to arise. So, employers started setting-up “welfare offices” and “welfare secretaries” to manage activities like factory washroom, and safety issues.
By 1900 employers started setting-up hiring offices, training programs and factory schools.
New union laws added in 1930s. Equal employment opportunities matters emerged in 1960s. and globalization concept in 1970s. These trends make HRM more important.
Distributed HR and the new Human Resource Management:
HR and Strategy:
HR and Performance:
HR and Performance and Sustainability:
HR and Employee Engagement: