
Chapter Outline
· New Product Development Strategy.
· The New Product Development Process.
· Product Life-Cycle Strategies.
· Additional Product and Service Considerations.
A company can achieve new product through two ways, which are as follows;
· Acquisition: it is to buy a whole company, patent, or license to produce someone else’ product
· New Products Development: The development of original products, product improvements, product modifications and new brands through the firm’ own product development efforts.”
New products are important for both, customers and marketers who serve them. They bring new solutions for their problems and variety to customer’ lives and these new products are a key source of growth for companies. In today’s fast-changing environment, many company’ growth depends on new products.
Innovation is Expensive and Risky:
A study found that, around 60 percent of all new consumer packaged products introduced by big and established companies fails. Two-third of new product concepts are never launched even. There are several reasons of this failure, which are as follows;
· Idea may be good; company may overestimate market size.
· Product is poorly designed.
· Product is not positioned well, or launched at wrong time.
· Overpriced.
· A high-level executive pushed for the development of new idea, ignoring poor marketing research findings.
· Development costs are higher than expected.
· Competitors give tough time than expected.
Important Points to keep in Mind:
Companies must understand its consumers, markets, competitors and develop a product that deliver superior value to customers.
Rather than taking risks and leaving new products to chance, companies should device strong new product planning and set-up a systematic, customer driven new product development process for finding and growing new products. It includes eight major steps, which are shown in figure;
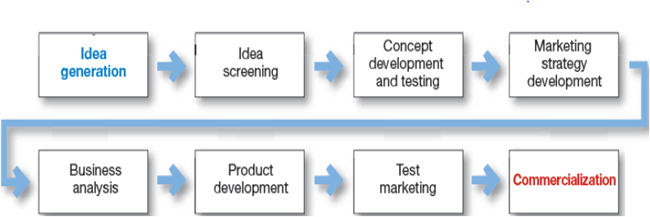
I. Idea Generation:
New product development process starts with idea generation. It is systematic search for new product ideas. Companies generate hundreds, even thousands of ideas, to find the most suitable and best one. These ideas come from internal sources and external sources, which are, customers, suppliers, distributors and competitors and others.
Internal Idea Source:
Using internal sources companies can find new ideas through formal R&D. for example, Ford has set-up an innovation and mobility center in Silicon Valley, it includes engineers, scientists and app developers. They work on everything from driverless cars to working with nest apps that enable consumers to control home heating, lighting and appliances from their vehicles.
Another internal source is, a company can use the brain of their own employees, they may be salesperson, to scientists, to engineers etc. Many companies have developed internal social networks and intrapreneurial programs to encourage employees to come-up with new product ideas. For example, AT&T has internal online innovation community, since its establishment in 2009, AT&T employees has have submitted more than 28,000 new ideas, and company has funded more than 75 projects.
External Idea Sources:
Companies can also get new product ideas from external sources, which are;
· Distributors: Distributors are there in the market and near to customers, they know about the needs and problems of customers, they can pass this information back to companies to develop a new product which can better serve consumer needs.
· Suppliers: Suppliers can tell companies about the new ways of manufacturing products, about new materials and techniques etc.
· Customers: Companies can use customer reviews, questions and complaints about the product to develop a better product to solve their problems in coming future. Or companies can gather them at some place to get some new idea.
· Competitors: Companies can carefully watch TV ads of their competitors to get an idea and develop their own a new product.
Other idea sources include, business magazines, seminars, webinars, websites, marketing research firms, advertising agencies, Universities, etc.
Crowdsourcing:
It is a broader approach of getting a new product idea, Crowdsourcing is to invite broad communities of people, employees, customer, independent researchers and scientists and even public at large, into a new product innovation process. It can produce unexpected and powerful new ideas.
II. Idea Screening:
The purpose of idea generation is to get maximum number of ideas, the later steps will reduce the number. The first idea-reducing stage is Idea screening. It helps spot good ideas and skip the bad one as soon as possible, as product development is a costly step.
In many companies, executives list down the ideas in a given standard format, that can be reviewed by new product committee. It touches the important points, estimated market size, product price, manufacturing cost, development time and rate of return.
One marketing expert presented three questions to ask before the developing the new product idea further, and the answer should be in “yes”. Questions are R-W-W (Real, Win & worth doing)
· Real: Do the need is real, will customers will buy it, do the new product will solve the customer’s problem.
· Win: Do the product will provide competitive advantage, do the company have enough resources to make the product.
· Worth doing: Do the product will help the company to grow. Does it have sufficient profit potential.
III. Concept Development and Testing:
An attractive idea should be developed into a product concept there are three different things;
· Product Idea: The idea for a possible product, that a company will offer into market.
· Product Concept: It is the detailed version of idea, described in meaningful consumer terms.
· Product Image: It is how consumers perceive an actual or potential product.
Concept Development:
It is to evaluate the customer’ reactions about your product or service before its launch. See, whether customers like your concept or not, how many customers (customer market) will buy it.
Concept Testing:
It is to test new products with group of consumers. The concept may be presented physically or symbolically to consumers. Customers asks question, concerned personals answer those questions. In the end it is observed, out of total, how many customers show 100% interest in the concept or how many have shown 50% interest and how many of them has rejected the concept.
IV. Marketing Strategy Development:
It is to develop initial marketing strategy for introducing a product into market. Marketing strategy statement consists of three parts, which are;
· First part describes, the target market, sales, market share and profit goals for the first few years.
· Second part describes, products planned price, distribution and marketing budget for the first year.
· Third and final part or marketing strategy statement highlights the planned long-run sales, profit goals and marketing mix strategy.
V. Business Analysis:
In this step, concerns review the sales, costs and profit projections for a new product to find out, whether they satisfy company’ objectives.
· To estimate sales, company may review the sales history of similar products and conduct market surveys. Company can also estimate minimum and maximum sales to assess the involved risk.
· While estimating costs, includes marketing and R&D cost, operations, accounting and financial costs.
After estimating sales and costs, company can analyze the new product’ financial attractiveness.
VI. Product Development:
In this stage, R&D and engineers develop the product concept into a physical product, to ensure that the product idea can be turned into a workable market offering. It is a call for huge jump in investment.
R&D department will develop one or more physical versions of product concept. It may develop a prototype first, which will satisfy and excite consumers and this can be produced quickly and at budgeted cost. Developing a complete and successful prototype may take days or weeks or even years.
Often product pass through rigorous tests to ensure safety and its efficiency. Companies can do this testing on their own or outsourcing this testing to companies specialized in testing.
VII. Test Marketing:
At this stage, product and proposed marketing program are tested in realistic market settings. Test marketing lets the company to test the product and its whole marketing program.
Test marketing costs can be higher and there are chances that competitors will take advantage. Which level of test marketing is required; it varies with each new product.
If big investment and great risk is involved or when managers are not sure about the product or its marketing program, then companies do a lot of test marketing. For example, Starbucks took 20 Years in developing Starbucks VIA instant coffee and spent several months in testing this new product in its shops in Chicago and Seattle before launching it nationally. The testing paid back, and now Starbucks VIA generating more than $300 million annually.
A company may do little test marketing, when managers are confident about the product or its marketing program, when product is less costly or in line extensions or while coping competitor’s successful products.
Companies may also shorten or even skip the test marketing after analyzing the market situation or a quick opportunity available in the market. For example, Starbucks very quickly introduced a mobile payment app in the market and with time remove the bugs found in the app.
Companies can also use controlled test markets or simulated test markets to reduce the cost and speed-up the process.
· Controlled Test Markets: it is to test new products or its tactics among controlled panels of shopkeepers and stores.
· Simulated Test Markets: in this, managers observe consumer response toward new products and marketing program in laboratory stores or simulated online shopping environment.
VIII. Commercialization:
After the successful test marketing, company finally decides to launch the new product in the market. Company starts with commercialization, to introduce the new product in the market, it involves high costs.
For Example, while introducing Apple Watch, Apple spent around $38 million on TV advertising campaign in its first year.
While launching a new product company must decide about its timing and where;
Timing:
· If the new product will eat the sales of company’ other product, then the launch can be delayed.
· If improvements are required in the product, launch can be delayed.
· If economy is down, launch of new product can be delayed.
· When competitors are ready to introduce a competing product then company may push to introduce the product sooner.
Where:
It is up to the company strategy or its expansion policy, company can introduce the new product in a specific region, the national market of international market. Example: Apple launch its products in 115 countries within the three months of its launch.
Managing New Product Development:
The new product development involves more than just going through above-mentioned steps. Successful new product development requires a customer-centered, team-based and systematic effort.
Customer-Centered New Product Development:
To make the new product successful, companies need to fully understand the customer needs and what he values. A customer centered new product development puts its all focus on finding new ways to solve the problems of customers and create more customer satisfying experiences.
One study found that, a successful new product are the ones which are differentiated, solve major problems of customers and offering them a compelling value proposition.
Another study found that, companies who involve customers in their new product development process have shown three times growth in income to those companies who don’t. customer involvement has very positive effect on new product development process and product success.
Team-Based New Product Development:
A successful new product development requires a total-company, cross-functional effort. Some companies use Sequential product Development, it is a process that we discussed earlier, a product is passed from each department, and product or idea moves on step by step, there is no bypass or overlaps. In todays fast changing environment, through this process companies keep control on complex and risky projects, but it can be dangerously slow, it can result in product failure, lost sales and profits.
To counter this problem, companies are using Team Based New Product Development, in this approach, cross-functional teams (people from marketing, finance, design, manufacturing or legal department etc.) work together, overlapping steps. It saves time and increase effectiveness.
Companies should use both customer-centered and team-based approach to gain a big competitive advantage to get the right new product into market faster.
Systematic New Product Development:
A new product development process should be holistic and systematic, it should use Innovation Management System, to gather, evaluate, review and manage new ideas.
Companies can appoint a senior employee as its innovation manager, this can be a web-based idea management software. It will encourage all stakeholders, employees, distributors, suppliers to participate in finding and developing new products. A recognition program can also be introduced to reward those, who contribute the best idea.
This will yield two favorable outcomes, first, it helps companies to create an innovation-oriented company culture. Second, it will help to get larger number of new ideas and to choose the best among them.
Every company wishes its product to enjoy a long and happy life. Company don’t expect to product to sell forever but to generate sufficient income, to cover all the effort and risks that went into launching it. Every product has a lifecycle but its shape can not be concluded in advance.
A typical life cycle has five district stages, which are shown in figure mentioned below;
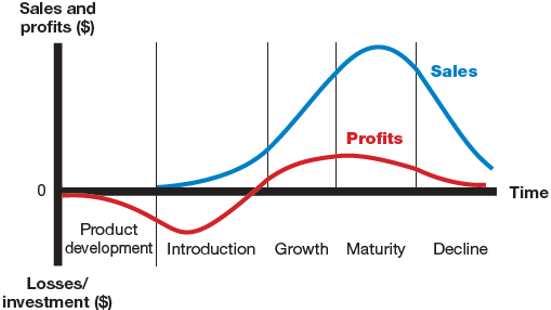
· Product Development: It is a stage, when company finds and develops a new product idea, at this stage sales are zero and investment cost is high.
· Introduction: Product is introduced in the market, sales growth is often slow, companies don’t think about profits in this stage due to expenses occurred in product development.
· Growth: The period of rapid market acceptance and increased profits.
· Maturity: it is a stage when sales become stagnant, as product has been accepted by most potential buyers. Profits often level off or decline, as marketing expenses increases.
· Decline: finally, the period, when sales fall and profits drop.
All products don’t pass through all these five stages, some products got decline just after its introduction, some products for long long time in maturity stage, some products go to decline and jump back to maturity stage with the help of strong marketing and repositioning. So, we can say, a well-managed brand could live forever.
For Example, Gillette and Coca Cola are still strong in the market their competitors, even after more than 100 years of introduction.
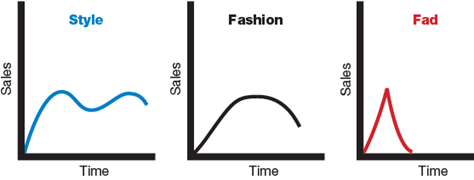
PLC concepts can be applied on Style, Fashion and Fads.;
Style: style is a distinctive mode of expression, it appears in clothing, art etc. once a style is invented, it may last for generations. Style has a cycle showing several periods of renewed interests.
Fashion: Fashion is a popular style in a given field and is currently accepted. It grows slowly, remains popular for some time and then declines slowly.
Fads: these show unusual growth in sales, it may be due to customer enthusiasm and immediate product or brand popularity.
PLC can help companies to develop good marketing strategies for different stages of life-cycle. To forecast product performance by using PLC may bring some practice problems. For example, it is difficult to forecast the sales of product at every PLC stage, length of each stage or the shape of PLC curve.
The moral can be concluded from PLC is that, companies should continue its efforts to innovate, otherwise they risk extinction. Because, no matter how successful a product is today, no one can rightly predict how it will perform in future. It may be due to strong competition, or consumer taste etc.
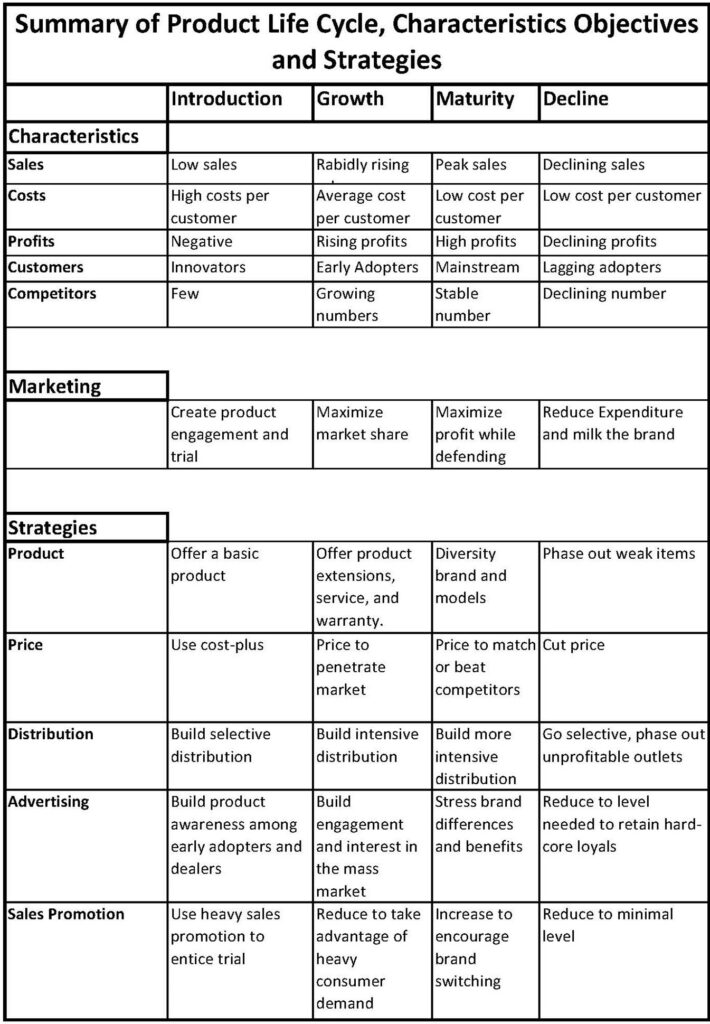
Introduction Stage:
· Introduction stage is when a product is first launched in the market.
· It takes time and growth of sales is slow. For example, frozen products took so long to get in the rapid growth stage.
· Profits are low or even negative.
· High promotion and distribution expenses.
· So much money is invested in building inventory and to attract distributors.
· Firms first make their attempts on most potential or ready to buy customers.
Strategies:
Companies should adopt launch strategies; right positioning should be the main focus.
Growth Stage:
After successful introduction in the market, a product enters the growth stage, this is the stage, where sales start climbing quickly.
· Early adopters will continue to buy, and later buyers will make their first purchase after hearing favorable reviews about the product.
· After watching the success of product, rivals will jump in the competition, with their products. This will expand the market.
· This expanded market will let companies to increase their number of distribution outlets.
· Prices remain same or decreases slightly.
· Spendings on promotion remains same or increases.
· Keep educating customers, along with the major goal of meeting competition.
Strategies:
Companies use different strategies to sustain rapid market growth for as long as possible.
· Improving product quality and adding new features in the product.
· Introducing new models.
· Entering new market segments and developing new distribution channels.
· It lowers the prices at some point to attract more customers.
Maturity Stage:
after passing through growth stage, product enters the maturity stage, where its sales will slow down.
· Product remains in this stage for longer time than in any other stage, and so, it poses serious challenges for marketing management.
· When slowdown of sales is observed of some product this raises competition in the market.
· This increase in competition will lead companies to lower the prices.
· Companies increase advertising budget, and development budget, so to introduce new features in the product, to keep the product alive.
· This surely will lead to profit drop. So, weaker competitors will start leaving, and in the end just well-established competitors will remain in the market.
Strategies:
Managers need to consider modifying the market, product offering and marketing mix to stay for long in the maturity stage.
· Modifying the market: It is to find new users and new market segments for its brand to increase the consumption of product.
· Product Offering: it is to add more features in the product, or enhancing its quality, changing its style, or packaging or technological improvements to retain existing customers and attract new ones.
· Marketing Mix: it is to increase product attractiveness by improving one or two or all the four Ps (Product, place price, promotion).
Decline Stage:
It is a stage, where product’s sales fade away. It may suddenly go down to zero or may get low and gets low for many years. Decline of any product can come for following reasons;
· Technological advancements.
· Consumer tastes
· Increased competition.
To carry the week product will incur cost, takes a lot of management time, there are many hidden costs, need big promotions and most importantly the failing product can hurt the image of company badly, which may greatly affect the sales of company’ other products.
Strategies:
· Companies must give at least one chance to product, and make efforts to bring it back in growth stage.
· To harvest the product, it is to cut various costs like, maintenance cost or R&D cost.
· Second strategy, a company can opt to identify the failing product and discontinue it.
Product Decisions and Social
Responsibility:
Marketers need to carefully consider public
policy and regulations regarding acquiring or dropping products, product
quality and safety, patent protection, and warranties.
·
Governments
may prevent companies from product line extension through acquisitions to keep
the competition in the market.
·
To
make the exact copy of competitors products is also declared illegal.
·
Companies
must also be aware of having legal obligations to their suppliers, dealers and
customers who have stakes in the dropped product.
·
Different
authorities are established to ensure the product quality and safety standards.
For example: GM so far has paid more than $2 billion in fines and
settlements, due to faulty ignition switches, which has caused deaths of more
than 120 drivers. Companies now hire Product Stewards, whose job is to
protect consumer form harm and also to take proactive measures and pointing out
potential product problems.
International Product and Services
Marketing:
International product and service marketers
face different challenges. They need to decide, what product and services to
introduce and in which countries. Second, they need to decide, how much to
standardize or adapt the products and services for international markets.
Companies want to standardize their
products or services. Standardizing a product helps companies to develop a
consistent image worldwide. It also lowers the costs of product design,
manufacturing and the cost of product marketing.
On the other hand, people of different
countries vary with their tastes, nature, likings and preferences etc. So, to
cope with these differences by adapting their product offerings.
Example:
McDonald’s operates in more than 100
countries. To attract the people in different countries, McDonald’ offer
adaptive burgers, like, in Pakistan they offer chicken and Beef burgers, in
Thailand they offer pork burgers, in China they offer mashed-potato burgers
etc.
McDonald’s also design the restaurant
differently in different countries, as people in France use to spend around
four times what an American customer spends per visit. So, the sitting space
and style of restaurant is designed accordingly.
Service Marketers:
Service marketers also face different
challenges in international markets. Commercial banking was first to grow
global. They provide global services to meet foreign exchange and credit needs
among people of different countries.
Germany’ Deutsche Bank serves more than28
million customers, through more than 2700 branches in more than 70 countries.