
Chapter Outline
· Compare and contrast views on the change process
· Classify types of organizational change.
· Explain how to manage resistance to change.
· Discuss contemporary issue in managing change.
· Describe techniques for stimulating innovation.
Change is an organizational reality.
Organizations face change because external and internal factors create the need for change.

Two view of change process:
a) The calm water metaphor:
In calm water metaphor change is occasional disruption in the normal flow of events.
Kurt Lewin’ three step change process has best explained this metaphor,

As per him successful change can be planned.
It requires unfreezing the status quo, changing to new state, and refreezing to make the change permanent.
Unfreezing be taken as preparing for change.
It can be done by increasing driving forces, that push change.
And by decreasing restraining forces that resist change.
Once unfreezing is done, introducing Change is easy process.
Now the Refreezing stage is important.
Because change can’t stand long until it is refrozen.
Unless this last step is done, there are strong chances that organizational employees will adopt the previous routine.
It’s a calm water scenario where change is planned and disruption is expected. Once disruption is dealt, implementing change is easy thing to do.
a) White-water rapids metaphor:
Change in this metaphor is not occasional or temporary.
It’s consistent with a world that’s increasingly dominated by information, ideas and knowledge.
We can take example of telecom companies, operating in Pakistan.
They face intense competition in the industry, technological changes, customer retention through different promotions, etc.
Today any organization that’s taking change as occasional and temporary is at great risk.
Too much is changing too fast for organizations or its managers to be complacent
It’s no longer a business is usual.
And managers must be ready to tackle any change efficiently and effectively.
What is organizational change?
In an organization managers use to change different things, that’s called organizational change, that’s may be alteration of people, or structural or technological change.
The person who brings change can be anyone, manager or any other employee, internal or external consultant.
The person who brings change is called as Change Agent.
Most of the organizations hire consultants to bring the change in organization, as they are external so they have a perspective that may lace in internal employees.
But they have limited knowledge about the organization, so they may try to bring drastic change in organization, because they don’t have to stay in organization after change is implemented to face the consequences.
In contrast internal managers are more thoughtful in this perspective, because they have to live with the consequences of their decisions.
Types of change:
Managers face three types of change

a. Changing structure:
Changes occur in external environment or in organizational strategies bring changes in organizational structure.
2 aspects of organizational structure are how work will be done, and who will do it.
Managers can alter both of these aspects or any one of these.
For example,
· Different departments can be combined.
· People under someone’s supervision can be increased or decreased.
· More rules and procedures can be implemented to increase standardization.
· Or employees can be given more to power in decision making.
b. Changing technology:
Technological changes can be made in
· New equipment, Tools, Operating methods (Coal mines)
· Automation (use of robots)
· Computerization (use of scanners in marts)
c. Changing people:
Changing people is to change the attitudes, expectations, perceptions and behaviors of people, which is not easy to do.
Organizational development is the term used to describe different change methods that focus on people and quality and nature of interpersonal work relationship.

We know it’s better for us to eat healthy and to be active, still most of us don’t do so, we don’t eat healthy food and don’t exercise, even we ignore stairs and use elevators and escalators.
Change can be a threat to people working in an organization.
People can adopt change if it’s made appealing.
Why do people resist change?
There are four main reasons, why people resist change,
Uncertainty.
Habit.
Concern over personal loss.
Belief that the change is not in organization’ best interest.
a). Uncertainty: for example, if quality control methods are introduced to manufacturing unit, quality control managers will have to learn some new techniques in this regard. For this they are often uncertain, whether they would be able to adopt new techniques or not, and possibly develop negative attitude towards change and act poorly if required to use them.
b). Habit: whatever we do in our routine life, habit has a major role in it.
Even while going to office we use the same way to office, and if someday due to some reason we are forced to use a different way, even if it’s better, we don’t accept this little change, and we will be irritated and abuse etc.
We don’t want to change our habits.
We rely on habits or programmed responses.
So while facing any change our tendency to respond in our accustomed ways become a source of resistance.
c). The third cause of resistance is fear of losing something that is already possessed.
They fear the loss of money, power, authority, friendship or personal convenience etc.
This the fear old employees have due to which they resist change.
d). Final reason behind resisting change is employees think change is not in organization’ best interest.
for example: employee may think new procedure will reduce the product quality.
This type of resistance is beneficial for organization if made positively.
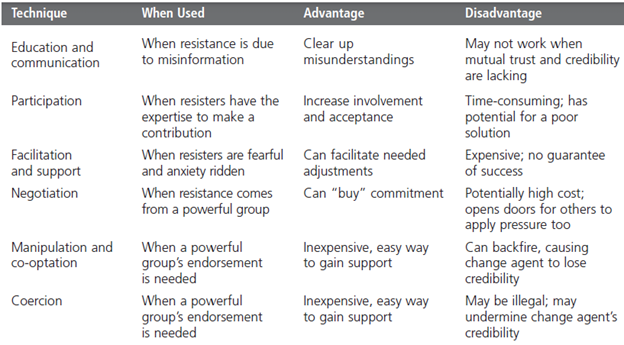
Techniques for reducing resistance to change:
a. Education and communication:
Managers can reduce resistance by providing logical answers to employees for change efforts.
Through this that type of resistance can be reduced which is created due to misinformation or poor communication.
b. Participation:
Involve such employees who are trying to resist the change in decision making process,
This will enable them to express their feelings, and will increase their commitment to the final decision.
c. Facilitation and support:
Pass such employees through counseling, therapy, new skill training to reduce their fear towards change.
d. Negotiation:
Exchange something of value (e.g. monetary benefit) for an agreement to accept change.
This can be so useful, if resistance comes from a powerful source.
e. Manipulation and co-optation:
It may involve distorting facts to make the change appear more attractive.
f. Coercion:
It is the extreme technique to handle the resistance, it may involve threats or force against the resisters.
Changing organizational culture:
Company’s culture takes so much time to form, once it’ formed, it has relatively stable and permanent characteristics that tends to make it very resistant to change.
Strong cultures are particularly resistant, because employees have become so committed to them.
Lou Gerstner, CEO of IBM (1993-2002) said that;
“I came to see in my decade at IBM that Culture isn’t just one aspect of the game—it is the game.”
Ø Understanding the situational factors:
What favorable conditions facilitate cultural change?
§ Dramatic crises occur:
For example, loss of major customer, financial loss, technological change in the industry, such things can enable the employees to think about the relevance of current culture
§ Leadership changes hand:
New leadership can introduce new value in the organization.
§ The organizational is young and small:
If the organization is small and young, it’s easier to change the culture as it is not mature and employees are not so committed to it.
§ Week culture:
Week cultures are also easier to accept change than the stronger ones.
Making changes in Culture:
Not a single action is enough to bring change, managers need to make a strategy to manage cultural change.
Organizational members don’t let go the values; they have association worked with.
Managers must stay alert, if someone return to old and familiar traditions.
Following are some actions, managers can take,

Employee Stress:
Most of people are under stress,
Employees facing stress range varies from country to country.
According to a study stress was the leading reason of people quitting their jobs, which employers were not taking seriously. Employers said stress wasn’t even among top 5 reasons why people leave their jobs instead they wrongly believed that insufficient pay was the main reason.
What is stress:
Stress is adverse reaction people have to excessive pressure placed on them from extraordinary demands, constraints or opportunities.
Stress is not always bad; it is good if it leads to success.
Two conditions are necessary for potential stress to become actual stress,
First there should be uncertainty about results and second results should be important.


What causes stress:
Factors that cause stress are called as Stressors, they may be personal or job-related factors.
Change of anything, personal or job related, bring stress with it, because it involves constraint, demand and opportunities.
Organizations have so many factors of creating stress for its employees for example, demanding quick and good results, unpleasant work place, irritating coworkers etc.
Five categories of organizational stressors are
Task demands
Role demands
Interpersonal demands
Organization structure
Organizational leadership
· Task demands
These are factors related with employee’ job. It can include, design of employee’ job, work place, co-worker, autonomy
· Role demands
It has 3 types, role conflicts, role overload, role ambiguity.
o Role Conflicts: In this manager expect such role from an employee, which is hard to perform and satisfy such expectations
o Role overload: expecting a lot of work from employee in which is impossible to perform in communicated time.
o Role Ambiguity: when managers have no clear expectations from employee. And on the other side employee is confused what he is to do.
· Interpersonal demands
It is a kind of pressure which is built due to lack of coordination among employees or colleagues.
· Organization structure
It can cause serious stress to employees, i.e. strict rules and getting zero involvement in decision making process.
· Organizational leadership
Managers create unnecessary tensions, fire employees, fear, anxiety for short term, tight controls etc. cause tension.
Personal factors can also be a source of stress, for example, family issues, personal economic problems or personality characteristics. Two traits of personality are Type A and Type B.
Type A Personality:
People with type A personality are
o often find in urgency with time and impatient.
o Comes under stress where competition is high.
o Difficulty accepting and enjoying leisure time.
Type B Personality:
Opposite of Type A is Type B personality.
o They are not so impatient.
o Don’t show so much urgency with time.
Employees with type A personality show more symptoms of stress, even if personal and organizational stressors are low.
Symptoms of Stress:
Employees facing stress may become more depressed and more argumentative
Stress symptoms can be classified into 3 general categories i.e., physical, psychological and behavioral.

In Japan there is a phenomenon that is called as “Karoshi”, which literally mean is “death from overwork”.
During the 1980’ many senior executives lose their lives without previous serious illness.
In this course Japanese ministry of labor get involved and now they publish stats on the karoshi deaths.
How can stress be reduced:
Stress can never be eliminated from a person’ life. Managers should;
· Hire the right person for the job.
· Improve organizational communication helps in reducing stress.
· Performance planning program such as MBO, it clarifies responsibilities, performance goals and reduces ambiguity through feedback.
· Job redesign can also reduce stress. i.e. make job competitive or reduce the work load.
· Redesign job in such a way that employees may start taking part in decision making process.
If stress is from employee’s personal life, it raises two problems,
· 1st, it’s difficult for managers to control it.
· 2nd it is unethical to ask someone about their about their personal life. If employee is responsive, then
Managers might consider several approaches to sort this problem.
· Employee counselling: it can provide stress relief; people often want to share problems in their minds.
· Time management program: if employees is having stress due to time management or assigning priorities.
· Wellness programs: health fitness facility at workplace.
Making change happen successfully:
Organizational change is an ongoing daily challenge for the managers.
Efforts from all levels of managers are required to bring change.
To make change happen successfully,
a) Make the organization change capable.
Link the present and the future.
Actively support and encourage day to day improvements and changes.
Encourage mavericks.
Shelter breakthroughs.
Integrate technology.
Build and deepen trust.
Couple permanence with perpetual change.
Support an entrepreneurial mindset.
b) Understanding their own role in the process.
Recognizing own role is very important.
Managers can and do act as change agents.
They may also be change leaders.
When organizational members resist change, it is manager’s duty to lead the change process.
Even if there is no resistance to the change, someone need to play the role of a leader.
c) Give individual employees a role in the change process.
To make change successful, all organizational members need to be involved.
Managers need to encourage them to become change agents.
And look for day to day improvements and changes that individuals and teams can make.
“Innovation is the key to continued success”
(Ajay Banga, CEO MasterCard)
“We innovate today to secure the future”
(Sophie Vandebroek, Chief technology officer, Xerox Innovation Group)
We can imagine the importance of Innovation from these two quotes.
Some examples of innovative companies are,
Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Google, Huawei, Walmart. Etc.
Creativity Vs Innovation:
Creativity is the ability of combining ideas in a unique way or to make unusual association between ideas. Creative organizations have unique ways of working. Creativity by itself isn’t enough.
Outcomes of creativity to be turned into useful products or work methods, which is called as Innovation. In innovative organizations when managers demand creativity from its employees, that means they want to stimulate and nurture innovation
Stimulating and nurturing innovation:
To get the desired outputs (Innovative products) requires transforming inputs. Transforming inputs need creative people as well as right environment to help transform those inputs into innovative products or work methods.
Environment that stimulates innovation have three variables,
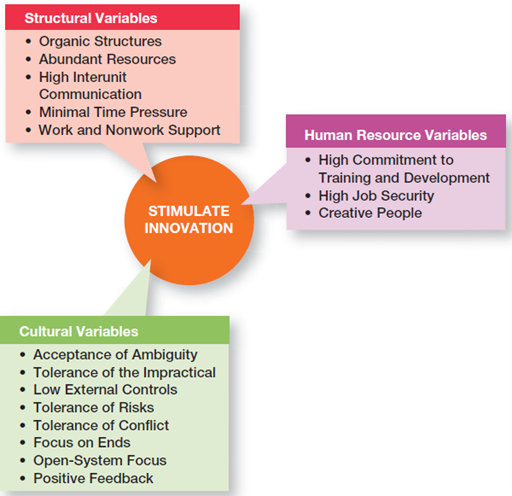
· Structural variables:
Organic structure:
This type of structures positively influence innovation.
As it has low work specialization, centralization and formalization.
So, it provides flexibility and sharing of ideas, which are needed for innovation.
Abundant resources:
Availability of abundant resources gives you large area to play.
As if companies have resources, they can do repeat experiments which will result in innovation.
High Inter-Unit Communication:
Communication gap should be reduced to zero between different organizational units.
This will enable employees to speak openly and share different innovative ideas of work or product design etc. in their minds.
Minimal time pressure:
Innovative ideas try to reduce time pressure o employees to work creatively.
Time pressure urge people to work harder and sometimes it’s but studies show that it results in less creative.
Work and non-work support:
Finally, support your employees in whatever they are doing and listen them what they have to say.
Give them proper feedback, encourage them provide them environment of open communication.
This will make them more creative than before.
· Cultural variable:
Innovative organizations have similar cultures for example, such organizations encourage experiments, reward both success and failures and celebrate mistakes.
Innovative organizations have following characteristics.
Accept ambiguity:
Too much focus on objectivity and specificity leads to creativity.
Tolerate the impractical:
Don’t show aggression to impractical behavior, there is possibility that, what we see foolish or impractical at first sight might lead to innovative solution.
Keep external controls minimal:
Where innovation is highly concerned, rules and regulations or other organizational policies are kept to minimum level.
Tolerate risk:
Taking risk is encouraged in innovative organizations. employees fear that it will provoke anger among employees who like the status quo. Or other employees will think negatively about him.
Tolerate conflict:
Different opinions from different employees is encouraged.
Focus on Ends rather than Means:
Ends or goals are pretty clear.
Employees are encouraged to take different routes to reach the destination.
There can be different right answers to same questions asked.
Use an open-system focus:
Employees are encouraged to take and absorb ideas from outside environment, from different cities or even from different cultures.
Then share new ideas in the office, which are not read or discussed in regular routine life and magazines.
Provide positive feedback:
Managers give encouragement and positive feedback to employees who come-up with new or unique idea.
Exhibit empowering leadership:
Show organizational members your confidence on them.
Make them realize that the work done by them is significant.
Tell them that you are confident that they can achieve high performance goals.
This will have positive impact on them and will make them more creative.
· Human resource variables:
Innovative organizations conduct trainings for their employees to make them stay updated, provide them job security for making mistakes and encourage employees to become Idea Champion.
Idea champions have same characteristics like, they are highly self-confident, energetic and risk takers.
They also exhibit leadership qualities. And gain support from other staff members.
They often have decision making discretions. This helps them introduce and implement innovations in the organization.