
Chapter Outline
· Model of Consumer Behavior
· Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior
· Buying Decision Behavior and the Buyer Decision Process
· The Buyer Decision Process for New Products.
Consumer Buyer Behavior:
It is the buying behavior of final consumers, individual and households, who buy services and products for their personal consumption.
Consumer Market:
It is a place from where final consumers buy products and services.
Consumers make so many buying decisions every day. Big companies conduct research to know the buying decision, to answer important questions, what consumers buy, why they buy, where they buy, how and how much they buy and when they buy. These questions are not easy to get answers, because the answers of these questions are often locked somewhere deep in consumer’ mind. And if is observed that often consumers themselves don’t know exactly what influences their purchase decisions.
First comes, how consumers will respond to marketing efforts of any company, then economic factors. These factors enter into the consumers black-box. Second, buyer’ characteristics, cultural, social, psychological and personal factors, then buyer’ own decision process effects his or her behavior.
The decision process from need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives to purchase decision and post purchase behavior, all this starts long before actual purchase decision and remains continue long after.

Consumers’ purchases are strongly influenced by cultural, Social, Personal and Psychological characteristics. As shown in the figure below,

Cultural Factors:
Cultural factors have deep impact on consumer behavior. Marketers should try to understand culture, subculture and social class, and role they play in buyer’ life.
Culture:
Definition: “Culture is the set of basic values, wants,
perceptions and behavior learned by the member of society from family and other
institutions.”
Example: Culture greatly influences the buying decision of an
individual. An American born child will learn values
like; practicality and efficiency, youthfulness, material comfort, health and
fitness etc.
Marketers always try to learn Cultural
shifts, in a society to know the demand of new products.
Example: 10 to 15 years back, it was considered very odd for a girl to wear a pant with short shirt in Pakistan, and now in 2022 it’s getting common. And we can expect its acceptance on larger scale in the years to come.
Subculture:
Every culture further consists of different
smaller subculture. Subculture is a group of people with shared value systems
based on common life situations and experiences. It includes different
religions, nationalities, geographic regions and racial groups.
Example: Hispanic Americans, African Americans and Asian Americans. If we talk about Pakistan, we have Sindhis, Punjabis, Pakhtoons and Balochis. They all vary in their tastes and clothing choices etc.
A Total Marketing Strategy:
It is a marketing strategy made to attract
all the population sharing similar needs. Regardless of subculture or
differences.
Example: In Pakistan brands like K&Ns, Sabroso and Menu they offer chicken made products to target the whole population. Because chicken is accepted in every religion.
Social Class:
Social class structure exists in almost
every society. These are ordered divisions whose members share similar
interests, values and behaviors.
Social scientist has identified seven
classes in America, these are; (i) upper-upper class, (ii) lower upper class,
(iii) upper middle class, (iv) middle class, (v) working class, (vi) upper
lower class and (vii) lower-lower class.
Social class is not classified on just one
factor, i.e., income. It is classified on the basis of education, occupation,
wealth, income and other variables. In some cultures, the lines among these
classes are so rigid and in some cultures are flexible.
Example: In America members of society can move from one
class to lower class but in Sub Continent this barrier is so rigid one cannot move
from one class to other easily.
Social Factors:
Consumer’ behavior is also greatly influenced by following social factors, which are consumer’s small groups, social networks, family and social roles and status.
Groups and Social Networks:
Groups:
o
Membership
Groups: these are the
groups to which a person belongs and have direct influence on person’ behavior.
o
Reference
Groups: “groups or individuals
that influence our beliefs, opinions, behaviors and attitudes.” Consumers take
them as their role models
o
Aspirational
Group: individuals are
often influenced by other groups; they want to be associated with other groups.
Marketers try to identify reference groups of their target market, so that they may influence the choices of consumers. The importance of reference group varies in respect with products and brands. It is stronger when the product is tangible and visible.
Word of Mouth Influence: It is the impact of personal words and
recommendations of trusted friends, associates, family and other consumers on
buying behavior. The influence of “word of mouth” happens naturally, when a
person buys something from brand, he will speak about it in one way or other.
One survey’ results show only 49 percent of people said that they believe or trust on advertisements and 72 percent of the people said they trust family, friends and 72 percent people said they trusted online reviews.
Opinion Leaders: These are the people within the reference
group, who have special skills, personality, knowledge or other
characteristics, exert influence on others. Some experts name them as leading
adaptors or influential.
Marketers try to identify these opinion
leaders for their products because when they speak, consumers listen.
Buzz Marketing: it is a viral marketing technique which has a purpose of maximizing the word-of-mouth potential of a product or campaign. This strategy initiates large-scale discussions on social media and in consumer’s families and friends.
Online Social
Networks:
These are online communities, where people
communicate, socialize, exchange opinions and information. it includes blogs,
message boards, social media sites, shopping sites etc.
Marketers are working hard to get maximum
out of these social networks and trying to grab opportunities to promote their
products and build closer relationships with customers rather than throwing
one-way commercial messages at customers.
Example: Telecommunication company in
Pakistan, Ufone have Facebook chat team to solve customer queries through chat
and to make the bond more stronger with the customers.
Family:
Family plays important role in buying
decisions. In earlier times grocery and clothing were considered as the job of
females but in recent times as females has started jobs so the ratio has
changed dramatically.
Example: as per a survey, in US, 41% of men
do grocery, 39% of men do laundry and about one quarter said that they are
responsible for the cooking at home.
This changing ratio of responsibilities and
influence have forced marketers to review their marketing strategies, now they
are targeting the opposite sex to sale the products.
Even children have great influence on
family purchases, now 70-71% of children guide parents where to spend money and
free time, 64% decides where to spend vacations, 58% guide what to eat and from
where and 43% tell parents where to live.
So, marketers should develop marketing
strategies keep these changing numbers in mind.
Roles and Status:
An individual belongs to different groups,
clubs, online communities and organizations. Where he has different roles and status.
A role consists of different activities an individual performs and each role
reflects his status in the group or organization.
Example: A person is a manager in the organization, a father
at home, a fan in games etc. so he buys products which are required by his role
in different occasions. In office he may wear formal dress, at home he may wear
trouser shirt and at some game he may wear the shirt of his favorite team.
Personal Factors:
Personal factors such as occupation, age and stage, economic situation, lifestyle, and personality and self-concept also influence the buyer’s decisions.
Occupation:
An individual’ occupation plays an
important role in the buying of products and services. A white-collar worker
would prefer to buy formal dresses, while blue-collar employees prefer rough
and tough clothes.
Example: CAT/Caterpillar make rugged mobile phones for the
employees who do challenging jobs, especially in construction sector. CAT’
phones withstand extreme drops and temperatures, enhanced audio quality for
noisy workplaces, display that can be controlled with wet fingers and gloves
and are dust and water proof.
Age and Life Stage:
Buying priorities of individuals change
with age. Tastes in food, furniture, clothes are often age related. Buying
cycle life also play part in shaping buying priorities and these life-cycle
changes results from demographics and life-changing events, marriage, buying a
home, having children, change in income, divorce, moving out of home and
retirement.
Understanding the life stage helps
marketers to better find, understand and engage consumers. With this
information about the consumer life stages, marketers can create targeted,
actionable and personalized campaigns based on how people consume and interact
with brands and the world around them.
Example: Children in their childhood love to buy more and more toys, but when they grow up, they don’t even visit toy shops.
Economic Situation:
An individual’ own economic situation
influences his buying priorities. Marketers watch trends carefully in personal
income, spending, interest rate and savings. Companies now repositioning,
repricing and redesigning their products and services. Companies attracting
consumer by saying “expect more, pay less”.
Example: Almost every smartphone brand is now offering low-cost
cell phones for both at home and in the world’ emerging economies.
Lifestyle:
Lifestyles is described as individual’
pattern of living as expressed in major AIO dimensions, which are Activities
(work, hobbies, sports, social events and shopping), Interests (fashion,
food, recreation and family) and Opinions (about themselves, business,
products and social issues).
The Individuals from different cultures,
subcultures, social class or occupation may have different lifestyles. Lifestyle
is individual’ complete pattern of acting and interacting in the world.
Consumers not only buy products; they buy
vales and lifestyle those products represent. Marketers try to identify
lifestyle segments with needs which can be served through special products or
marketing approaches.
Personality and Self-Concept:
Personality is defined as the unique
psychological characteristics that distinguish a person or group. Its traits
are self-confidence, dominance, autonomy, sociability, adaptability,
defensiveness and aggressiveness.
Individual’ distinct personality influences
his or her buying behavior. Personality of a person is useful for marketers to
know his or her behavior for certain product or brand choices.
Brands also have personalities, and
consumers choose brands with personalities that match with their own. A
researcher has identified five brand personality traits:
·
Sincerity: (honest, cheerful, down-to-earth,
wholesome)
·
Excitement: (daring, up-to-date, spirited and
imaginative) Example, Apple
·
Competence: (intelligent, reliable and successful) Example,
Washington post
·
Sophistication: (Charming, glamorous, upper-class),
Example, Gucci
· Ruggedness: (outdoorsy and tough) Example, Ford F150
Self-concept or Self-image: it is to say that person’ possessions
contribute to and reflect their identities. We are what we consume. So to
understand consumer behavior marketers need to understand the relationship
between consumer self-concept and possessions.
Psychological Factors:
There are four psychological factors which influence person’ buying choices, which are: motivation, perception, learning and beliefs & attitudes
Motivation:
A person may have several needs at a given
time, these needs may be biological (hunger, thirst, discomfort), or
psychological (need for recognition, esteem or belonging).
A need becomes motive when it is aroused to
a sufficient level of intensity. Motive or Drive is a need which
is sufficiently pressing to direct the person to seek satisfaction.
Many psychologists have presented theories
of human motivation, two of which are more popular, one is presented by Sigmund
Freud and second is presented by Abraham Maslow.
Sigmund Freud theory of motivation: Sigmund Suggested that, person’ buying
decisions are often guided by subconscious motives, that even buyer don’t fully
understand. He assumes that people often don’t know or can’t describe why they
act as they do. They are unconscious about the real psychological forces which
are shaping their behavior.
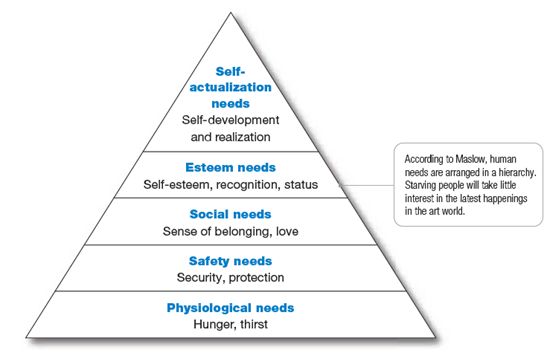
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Maslow developed hierarchy of needs, to
explain why people are driven by specific needs at particular times. A person
tries to satisfy most important need first and when that need is satisfied, it
is no more a motivation, then the person will try to satisfy the next most
important need.
Perception:
It is a process by which people select, organize and interpret information to form a meaningful picture of the world.
People build different perceptions of the same stimulus because of three perceptual processes: selective attention, selective distortion and selective retention.
· Selective Attention: The tendency of people to get maximum information out of what they see. So, marketer need to work hard on grabbing consumer attention.
· Selective Distortion: It is to say that, people interpret information in a way to support their set beliefs.
· Selective Retention: it means, people remember good and positive points about their favorite brands and don’t even bother the good things about the competing brands.
Subliminal Advertising: these are visual or audio stimuli which the conscious mind cannot perceive.
Example of Subliminal Advertising:

It’s a famous Ice-cream brand. It shows a hidden message in its logo i.e., BR, it also says 31 (in pink) flavors of ice-creams.
Learning:
Learning is when changes in person’ behavior occurred from experience. People learn, when they act. Learning depends upon drives, stimuli, cues, responses and reinforcement.
· Drive: It is an internal stimulus which calls for action.
· Stimulus Object: a drive becomes motive when it is directed towards a particular stimulus object.
· Cues: these are minor stimuli which determines where, when and how a person responds.
· Response: all cues then influence a person’ response, to take some decision.
· Reinforced: if the decision went right, person will recall it again and again, its reinforcement.
Example: A person’ drive for self-actualization may motivate him to purchase a camera (stimulus object). Camera brands, special price offers are minor cues. These cues will influence person to generate a response. If the purchase of camera was right consumer will use it again and again, that is reinforcement.
Beliefs and Attitudes:
Beliefs: are thoughts that the person holds about something, these are often knowledge, opinions and faith based and don’t carry emotional charge.
Marketers want to know the beliefs of customers hold about their products and services because these beliefs build product and brand image and effects the buying behavior. If these beliefs are negative or wrong, marketers initiate different programs and campaigns to correct them.
Attitude: “it is individual’ favorable or unfavorable evaluations, feelings and tendencies toward an idea or object.”
“Attitude is one’ behavior and the way of coping with the things he deals in daily life.”
Attitudes put people in a frame of likings or disliking things, of moving towards or away from them. Attitudes are difficult to change, so companies try to fit their products with the existing attitude patterns rather than attempting to change them.
Types of Buying Decision Behavior:
Buying behavior differs greatly for different products like, buying a face soap, smart phone, or buying a new car. More complex decisions involve more participants.

Complex Buying Behavior:
Individuals show complex buying behavior when they are highly involved in purchases and they find significant differences among brands. It happens when the product is highly expensive. For example: while buying a car.
While buying such a product, the buyer passes through learning process, first he develops his beliefs about the product, then attitudes and then makes a thoughtful purchase choice.
Marketers need to make every small information available about the product to customers, which will help customers to get answers of their queries and will make-up their mind about buying the product or not.
Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior:
This is a kind of behavior where consumers are highly involved, the product is expensive, infrequent and risky purchase, but there are very little differences among different brands.
For example: buying carpets for home or office.
As there are minor differences among different brands of the product, consumer may visit the market, check availability of products, compare rates and buy quickly.
Consumer prefer good price and purchase convenience.
After the purchase, consumer may experience Post Purchase Dissonance (after-sale discomfort), and hear favorable things about other brands. Marketers may provide after sale communications to avoid this discomfort and assist the consumer and feel good about the brand choices.
Habitual Buying Behavior:
People show low involvement and find little differences among brands. For example: table salt. People just go to nearest store and buy. Consumers show this behavior when the product is frequently purchased and low-cost product.
Consumers don’t pass through belief-attitude-behavior sequence, don’t search for brands as they are not highly involved. Consumers even don’t evaluate the product after the purchase. People don’t show brand loyalty so marketers use price competition and sales promotions or add features to products to differentiate it from competitors and attract customers.
Variety Seeking Buying Behavior:
Variety seeking buying behavior is when consumers show low involvement in buying a product but there are significant differences among brands. For Example: buying biscuits. Consumers don’t do much evaluation while buying biscuits but do evaluate during consumption.
Consumer do switch brand to avoid boredom or try some other brand, and don’t switch to seek variety.
Marketers can attract customers by keeping shelves fully stocked all the time, running advertisements, challenging firms offer lower prices, discount coupons, special deals, free samples and advertise in a way which encourage consumers to try something new.
The Buyer Decision Process:
The buyer decision process consists of five stages, which are shown in the figure and described below. Marketers need to focus on complete buying process rather than just on the purchase decision.

Need Recognition:
Buying process starts when the buyer recognizes need or a problem. It can be due to internal stimuli (hunger or thirst) or external stimuli (for example: watching an advertisement on TV.).
At this stage marketers should reach consumers and ask for their needs, wants and problems, when these needs arise and how consumers satisfy their needs.
Information Search:
Information search depends upon interested consumers. If consumer’ drive is strong and a satisfying product is available in the nearest market place, in this case he doesn’t need to go for information search. In other case, consumer will search for more information. For example, in case, if a consumer wants to buy a car.
Information search can be done from following sources.
· Personal Sources: (Family, neighbors, friends)
· Commercial Sources: (sales person, advertising, packaging, displays, etc.)
· Public Sources: (mass media, social media, peer reviews, online search, etc.)
· Experiential sources: (using and examining the product)
The most effective sources considered is personal, it provides legitimate or evaluate products to buyer. Where commercial sources normally inform the buyer.
In the result of information search, consumer’ knowledge about product and different brands increases.
Companies should design their marketing mix which can make prospects aware of knowledgeable about their brand. And also, carefully identify the consumer’ sources of information and importance of each source.
Evaluation of Alternatives:
After information search, next step is evaluation of alternatives, based on available information. How consumers process that information to choose among alternative brands. Consumers don’t use single, specific or single evaluation process in all buying situations, they use several evaluation processes.
This evaluation depends upon the individual consumer and specific situation. Sometimes, consumers do careful calculations and sometimes do very little or don’t even. Sometimes, consumers make buying decisions on their own and sometimes they seek advice from friends, family, sales persons, online reviews etc.
Marketers should always try to know what evaluative processes consumers adopt, so that companies may take steps to influence the buyer decision of consumers.
Purchase Decision:
In the evaluation stage, consumers rank brands, now it’s time to make the purchase decision. And more likely consumers buy the most preferred brand. But there are two factors that can come between the buying intentions and buying decision.
First is attitude of others, if consumer respect someone’ opinion, consumer will make decision following that opinion.
Second is unexpected situational factors, these are the factors like expected income, expected product benefits and expected price of the product. It also has the power of changing buying intentions. For example: if your close friend suggests to buy BMW car but your income affords Suzuki car, in this case you definitely will neglect the suggestion of your friend.
Post-purchase Behavior:
After the purchase of product, the consumer is satisfied or dissatisfied. It depends upon the relationship between consumer’ expectations and perceived performance of the product. The larger the negative gap between expectations and performance, the greater the consumer’ dissatisfaction. So, companies should promise what their products can actually deliver.
Why its always important to satisfy customer, because customer satisfaction is the key to building profitable relationship with consumers, to keeping and growing consumers and securing their customer lifetime value.
A dissatisfied customer will most probably no make repeat purchases and even can influence his family and friend’ buying decisions.
A New Product is a good, a service or an idea as perceived by some potential customers as new.
Adoption Process: It is defined as mental process through which a person passes from the first learning about an innovation to final adoption.
Adoption: Adoption is a decision by a person to become a regular user of the product.
Stages in the Adoption Process:
Adopting a new product includes five stages process.
· Awareness: Consumer knows about the new product but don’t have much information about it.
· Interest: The consumer collects information about the new product.
· Evaluation: the consumer evaluates, that it worth to try a new product, or it makes any sense.
· Trial: consumer tries the new product on smaller scale to realize the value of new product.
· Adoption: here consumer decides to make regular and full use of the new product.
This model suggests marketers, how they can help consumers to pass through this process, and make their adoption decision easier and quicker.
For Example: If consumers are considering company’ products, companies can offer sales promotions, free trials, providing more and more information etc.
Individual Differences in Innovativeness:
Every person is not always willing to try new things. They vary greatly in nature of trying new things. There are consumption pioneers, and early adopters then comes other people who adopt new products much later.
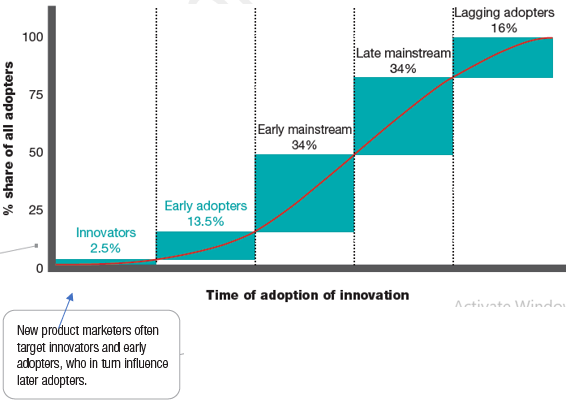
There are five adopter groups, which have different values.
· Innovators: They love adventures, always ready to take risks. They are just 2.5 percent of the consumers.
· Early adopters: They are opinion leaders; they adopt new products earlier but carefully. They are 13.5 % of total consumers.
· Early Mainstream: They rarely are opinion leaders; they adopt new products before average people.
· Late Mainstream: They are skeptical, they adopt new products only after a majority of people have tried it.
· Lagging Adopters: these are tradition bound people, they adopt new innovation when the product it becomes a part of tradition.
Marketer should always look for innovators and early adopters and direct initial marketing efforts towards them.
Influence of Product Characteristics on rate of Adoption:
Product characteristics effects its rate of adoption, some products receive outstanding response from consumers, For Example: Apple’ iPod, iPhone, iPad etc.
There are five important characteristics which influence an innovation’ rate of adoption.
· Relative advantage: The degree to which an innovation is superior to the existing product in the market.
· Compatibility: The degree to which innovation fits the values and experiences of potential consumers. For example: electric cars are not compatible with the nation’ current refueling network.
· Complexity: The degree to which the innovation is difficult to understand or use. Ease of use, user friendly etc.
· Divisibility: The degree to which innovation can be tried on limited basis. Test drive of new cars, free trials etc.
· Communicability: the degree to which the results and reviews of consuming a new product can be shared or described to others
The new product marketer must take deep research on all of these factors while developing a new product and its marketing program.