
Chapter Outline:
· Marketing Information and Customer Insights.
· Assessing Information Needs and Developing Data.
· Marketing Research.
· Analyzing and Using Marketing Information.
· Other Marketing Information Considerations.
Marketers need to take deep insight into what are customer’ wants and needs to create value and develop meaningful relationship with customers. These insights come from good marketing information. Companies use this information to develop a competitive advantage.
This customer insight is not easy to get, even customers themselves often don’t know exactly what they want. To better serve this purpose marketers must effectively manage marketing information from wide range of sources.
Marketing Information and Today’ “Big Data”:
Companies can gather information in greater quantity. Today, the world is full of information. Consumers themselves generate information through PCs, smartphones, tablets, mobile apps, social media platforms etc.
Big Data: the huge and complex data sets generated by today’ sophisticated information generation, collection, storage and analysis technologies. The data is so huge that managers are overloaded and often overwhelmed by it. That’s the far more information than any manager can digest.
Every year people and systems of the world together generate about a trillion gigabytes of information, which is enough to fill 2.47 trillion good old CD-ROMs, that means a stack tall enough to go to moon and back four times.
Example: if Apple or Coca Cola monitors blogs, social media posts, online discussions, it will be around 6 million public conversations a day and more than 2 million a year.
So, the problem is not with quantity of data, managers don’t need more information, they need better information or to make better use of the information they already have.
Managing Marketing Information:
The real value of marketing information lies in how it is used, in the customer insights, that it provides. Following this thinking, big names have restructured their marketing information and research function.
Companies must design marketing information effective enough that it provides managers the right information at the right time to create customer value, engagement and stronger customer relationship.
Marketing Information system (MIS): it consists of people and procedures which are dedicated to access information needs, developing the needed information, and to help the decision makers use the information to generate and validate actionable customer and market insights.
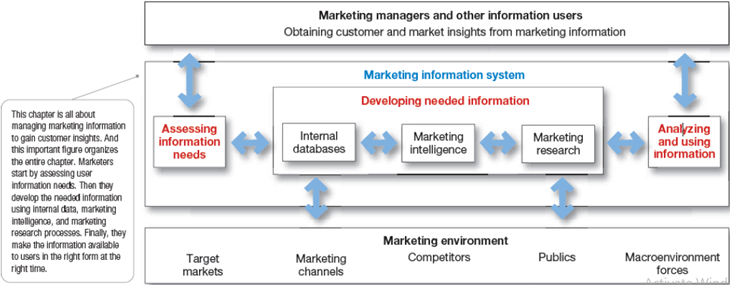
Assessing Marketing Information Needs:
Marketing Information system serves the company’ internal stakeholders i.e., marketing and other managers as well as external partners which are suppliers, resellers, or marketing services agencies. A good MIS balances the information users would like to have against what they need and what is feasible to offer.
In this age of big data, too much data can be harmful as too little. The MIS should monitor the marketing environment carefully and provide information and insights to decision makers to make key marketing decisions.
Companies must analyze whether the value of insights gained from additional information is worth cost of providing it. Cost of obtaining, analyzing, storing and delivering information can rises quickly, and both value and cost are often hard to assess.
Developing Marketing Information:
Marketers can get the required information from internal data, marketing intelligence and marketing research.
Internal Data:
Big companies maintain big internal data bases, i-e., collection of consumer and market information obtained data sources within the company’ network. Information can be obtained from many sources. Harnessing such bug data base can provide powerful insights and competitive advantage. Some are as follows;
· Marketing department provides information about customer characteristics, in-store and online sales transactions, social media and websites visits etc.
· Customer services department maintains the record of customer satisfaction and service problems related information.
· Accounting Department gives their input on records of sales, cashflows and costs.
· Operation Department looks for shipment and inventories etc.
· Sales Force provides information about competitors and reseller reactions.
· Marketing channel Partners reports on sales transactions.
Internal data bases can easily be accessed but can raise some problems. Such huge data is not easy to handle, data also age quickly to keep it current requires major efforts. Finally, to manage big data requires sophisticated equipment and techniques.
Competitive Marketing Intelligence:
It is to monitor, collect and analyze the publicly available information about competitors, consumers and developments in the marketplace. The objective of this competitive marketing intelligence is to improve strategic decision making by understanding consumer environment and their choices, assessing and tracking competitor’s’ actions, and to provide the alerts about opportunities and threats in the marketplace.
Marketing intelligence techniques includes observe consumers to questioning company’ own employees, online research, benchmarking competitors’ products, and watch carefully social media buzz.
Many companies use specialized teams to get mix with consumers to know, what consumers talk and think about their brands. And big brands like PepsiCo, Mastercard or Dell use sophisticated digital command centers to monitor routine brand related consumer and marketplace activities.
Much of marketing intelligence can be gathered from people inside the company, such as, executives, scientists, engineers, sales force and purchasing agents. Companies can also get important intelligence information from suppliers, key-customers and resellers.
Companies also have the option to subscribe with online data bases available, some are paid and some are for free. On these data bases there is large of useful data available for companies who need it.
Companies use marketing intelligence to regularly watch competitor’ activities i.e., their web and social media sites. It will help companies to prepare quick responses against competitor’ actions and moves.
Example: mobile companies regularly watch each other’ newly launched products, prices, product specifications etc.
This also has raised a problem for companies, it is of “information leak”. Companies should use marketing intelligence to protect the secret information. Example: companies can restrict employees not to post company related information on social media sites and then make a proper check on employees’ activities.
This growing use of marketing information has raised ethical concerns. Companies should take advantage of publicly available information and should not stoop to snoop. But with legitimate intelligence sources now, companies don’t need to break the law.
In addition, with marketing intelligence marketers often need more deep and formal studies, that provides important customer and market insights for certain marketing decisions and situations.
Marketing Research is the systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation facing an organization.
It provides important insights about customer motivation, purchase behavior and satisfaction. It also helps marketers to analyze the market potential and market share, pricing, distribution, product and promotional activities.
This marketing research can be done through company’ own research department or hire a third-party research team or by simply buying data from big data firms.
Example: Samsung want to know, how consumers will react towards its next generation products. In these situations, companies need marketing research.
Marketing Research process have following four steps. Will discuss each.
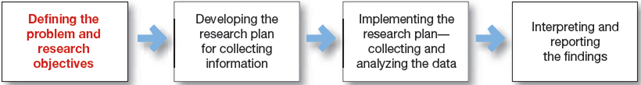
Defining the Problem and Research Objectives:
Defining a problem is probably the most difficult task, managers may feel that there is something wrong but don’t know the causes. And it goes more hazardous if the problem which is defined is not actually the real problem. So, marketing managers and researchers must work together to define the problem and agree on research objectives.
Once the problem is identified and research objectives are set, a marketing research process may have following three types of objectives, which are;
· Exploratory Research: it is to collect preliminary information which helps in defining problem and suggest hypothesis.
· Descriptive Research: this research describes things, such as market potential for a particular product or the demographics and attitudes of customers or consumers who buy the product.
· Casual Research: its objective is to test the hypothesis about cause-and-effect relationships.
Managers and researchers should put the statement in writing to be certain that they agree on the purpose and expected results of the research.
Developing the Research Plan:
After defining the research problem and objectives, now researchers must determine the exact information they needed, develop a plan to gather it efficiently and present the plan to management.
The research plan highlights sources of existing data and explaining specific research approaches, sampling plans, contact methods and instruments that researchers will use to gather new data.
The research plan should be presented in written proposal, it is more important when company is large or when the research is carried out by some third-party firm. The proposal should cover following points;
· The addressed problem by management.
· Research objectives.
· Information to be gathered.
· How results will help managers in decision making.
· And most importantly the research costs.
To gather the required information, managers can call for secondary data collection or primary data collection or both. let’s discuss each.
Gathering Secondary Data:
Secondary data consist of information which already exists somewhere, and was gathered for another purpose. And researchers often start by gathering secondary data, along with company’ internal data base, researchers can also opt to tap into a wide collection of external information sources. They can also buy data from outside sources.
Secondary data is easily and quickly accessible and at lower cost than primary data. Secondary sources often provide such useful data that hard to collect for an individual, either it would not be directly available or would be too expensive to collect.
· Commercial online databases: this is information available online from commercial sources or accessible through internet, researchers use these sources to conduct their own searches of secondary data sources. Beyond these paid sources there are industry associations, government sources or business publications offer free huge amount of information.
· Internet search engines: researchers can also get help from internet search engines to hunt relevant secondary information sources.
Problems with Secondary Data:
Researchers don’t get the complete information which is required for research. Researchers must evaluate the secondary data to make sure that data is;
· Relevant (satisfy the research project’ needs)
· Accurate (reliably collected and reported)
· Current (data is up-to-date)
· Impartial (objectively collected and reported)
Primary Data Collection:
Primary data consists of information gathered for some specific purpose at hand. After getting great help from secondary data, in most cases, companies must also collect primary data.
To collect primary data, researchers need to go through research approaches, contact methods, sampling plan and research instruments, as shown in the figure below, we will discuss each in details.
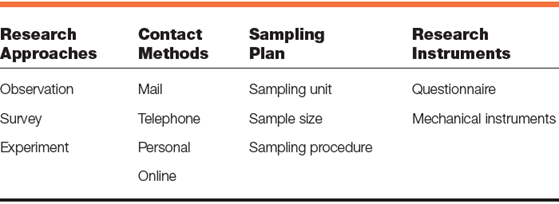
Research Approaches:
Research approaches to collect primary data includes observation, surveys and experiments. Let’s discuss each;
Observational Research:
It is to gather primary data (exploratory research) by observing relevant people, actions and situations. Researchers use to observe consumer behavior, it provides more customer insights rather than questioning them. Marketers not only observe consumer behavior but they listen them carefully what they are saying as well, they can listen customers from social media, blogs or websites.
· Ethnographic: It is a process, in which, companies send observers to watch and interact with consumers in their natural environment. These observers are highly trained, they may be anthropologists and psychologists or company’ own researchers and managers.
Observational and ethnographic research provides kind of details that cannot be emerged from traditional research questionnaires.
Observational approach has its limitations as well, like attitudes, motives and private behavior cannot be observed. Then observation is not easy to interpret into word or while compiling a report. So, researchers use observation along with other data collection methods.
Survey Research:
The widely used method for gathering primary data, this approach is also best suitable to obtain the descriptive information. Surveys are conducted when companies want to know about people’ attitudes, knowledge, preferences or their buying behavior, these are better found out by asking them directly.
Surveys are widely used due to its flexibility nature. It is used to obtain different kinds of information in different situations. Surveys can answer all the marketing questions or decisions can be made on phone.
Surveys have its limitations and problems,
· Sometimes people don’t often remember things which are asked in surveys.
· Sometimes people are not willing to answer the questions, or consider things as private.
· People often answer wrong, answer even when they don’t understand the question, just to pose themselves as smarter.
· Some people often avoid to answer due to their busy routine.
Experimental Research:
Experimental research is best suitable to gather casual information. Experiments involve selecting alike groups of subjects, giving them different treatments, controlling unrelated factors and checking for differences in group responses. We can say, experimental research tries to explain cause-and-effect relationships.
· Example: A fast food brand may use experiments to test the effect on sales of two different prices before adding a new sandwich in the menu. It can introduce the same sandwich in different cities at different prices.
Contact Methods:
Information can be gathered by mail, by telephone, by personal interview or online. Each contact method has its strengths and weaknesses.
Mail Questionnaires: These questionnaires are used to gather large amount of information at lower cost per respondent.
Strength of mail questionnaires are, (i) big data is received, (ii) people often provide honest answers and (iii) chance of bias answers is very low.
Weaknesses of mail questionnaires are these surveys are not flexible as these are in similar structure and questions are same for all respondents, response rate is slow, takes longer time to complete,
Marketers are trying to shift to faster, flexible and lower cost email, online and mobile phone surveys.
Telephone Interviewing: Strengths: Through telephone surveys, information can be gathered quickly and are far more flexible than mail questionnaires. Interviewer can skip some question willingly explain difficult questions to respondents to get the accurate answers. Response rate is higher than mail questionnaires.
Weaknesses are, (i) cost per respondent is higher than mail questionnaires. (ii) Some people may don’t share their personal things with interviewers. (iii) element of biasness is there, (iv)
Most of the people don’t want to receive unknow or sales or marketing calls.
Personal Interviewing: It takes further two forms, individual interviews and group interviews.
· Individual Interviews are often taken in streets, offices, shopping malls etc. Interviewer can guide the interview after analyzing the situation. These interviews are flexible. Interviewers can show packages or products about which interview is conducted. Interviewer can explain questions to respondents. These individual interviews are often three to four times costly than telephone interviews.
· Focus Group Interviewing: Group interviewing is to invite small groups of people to meet with a trained moderator to talk about service, product or organization. Moderator encourage talk freely and easy discussions to get in return deeper feelings and thoughts of participants. Participants are often paid for their time. As the moderator “focusses” discussion, so the name is focus group interviewing.
It’s becoming major qualitative marketing research technique to get fresh customer insights. Moderators observe people’ conversational flows, body movements, hear their opinions and group interplays. They also listen from behind the one-way mirror, video recording for later study or video recording if sitting far-off locations.
Challenges are, people participating in focus groups are often not honest, they hid their real feelings. It is very hard to generalize from results as they employ very small samples to keep time and costs down.
To overcome these problems, researchers are trying to modify the focus group design. Some companies are designing in a way to make participants feel relaxed to get more authentic response.
Immersion Groups: these are smaller groups of consumers who directly interacts with product designers without any moderator.
Online Marketing Research:
Internet has great impact on how marketing research is conducted. Now researchers are gathering data through online marketing research i.e., online focus groups, internet and mobile surveys, experiments, consumer tracking and online panels and brand communities.
A company can use internet and smartphone for following purposes;
· Questionnaires can be made on website.
· Mobile phones can be used to invite people.
· Online panels can be made for regular feedback, live discussions, or online focus group,
· Online experiments (different prices, headlines, or product features)
· Testing new products by establishing virtual shopping environment.
· Learning consumer behavior by tracking their click streams.
· It is well suited for quantitative research.
Advantages:
· It is cost effective
· As well as it saves time, it is far quicker than traditional and old research methods.
· It can reach respondents quickly and gets their response instantly.
· Once the questionnaire is set-up, now the cost difference is very little for 10 respondents and 10,000 respondents.
· With the help of internet, now any smaller company can conduct research and make their surveys using different websites (www.snapsurveys.com or www.surveymonkey.com,)
· Through internet it is now easy for researchers to reach hard to reach consumers like office executives, busy house-wives, etc.
· Qualitative research can also be conducted by using filters while selecting participants.
Drawbacks:
· It is hard to know, who is on the other side. It is very difficult to know, who is answering the questions being asked.
Online Behavioral and Social Tracking and Targeting:
Here marketers and researchers listen and watch consumers by actively tracking the unsolicited and unstructured customer information already available on the internet. Traditional marketing research provides logical consumer response to structured and intrusive research questions where online listening provides the passion and unsolicited consumer opinions.
Tracking consumers may include;
· Scanning customer reviews and comments.
· Using online tools to sort and analyze big data of consumer brand-related comments and messages, which consumers share on social media sites or blogs.
· It provides valuable insights about what consumers are feeling and saying about the brand.
· It helps to develop positive brand experience and relationships.
· More and more companies are now setting up social media command centers to utilize internet to get customer insights.
Behavioral Targeting: it is to use consumer tracking data to target ads and offers to specific consumers.
Example: if you add Samsung mobile in your cart on some shopping website, and don’t buy it, and later if you are trolling some website, you may see the ad of Samsung mobile that you did add to cart but didn’t buy it.
· Behavioral targeting: it tracks consumer movements across online site.
· Social targeting: it mine individual online social connections and conversations from social networking sites. Example, while using Facebook, you may see the ad of a wallet that your friend has just bought from some other website.
Sampling Plan:
Marketing researchers study small samples of total consumer population to draw conclusions about large groups of consumers.
Samples: It is a segment of population selected for marketing research; it represents the population as a whole. Ideally, the sample should represent the whole population, so that researchers can make accurate estimates of the behavior and thoughts of larger population.
Designing a sample requires three decisions;
· Who: Who is to be studied?
· How many: how much should be the size of sample.
· How: how the people in the sample be chosen.
Following are the types of samples;
Probability Sample:
· Simple random sample: Every member of population has a known and equal chance of selection.
· Stratified random sample : In this population is divided into groups (in regards with age, occupation etc.) and random samples are taken from each segment.
· Cluster (area) Sample: The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (such as blocks), and then drawing a sample of the groups to interview.
Nonprobability Sample:
· Convenience sample: Researcher choose the easiest member of population to obtain information.
· Judgment sample: researchers use their own judgment to choose members of population, who they think are good prospects for accurate information.
· Quota sample: the researcher finds and interviews a prescribed number of people in each of several categories.
Research Instruments:
Researchers use two main research instruments, i.e., Questionnaires and Mechanical Instruments to collect primary data.
Questionnaires:
Questionnaires are the most commonly used instrument, whether the research is conducted in person or by phone, by email or online. Questionnaires are very flexible. It includes questions, which may be open ended or closed ended.
Closed-ended questions include MCQs, it provides answers which are easy to interpret. And open-ended questions allow respondents to answer in their own words, Example; British Airways may ask travelers “what is your opinion about British Airways?”, it is mostly used in exploratory research to get the answers of “what people think”.
Instructions:
· Researchers should be careful in the use of wording and ordering of questions.
· They should use simple, unbiased and direct wording.
· Questions should be arranged in logical order.
· The first question should grab the interest of respondent and difficult or personal questions should be asked in the end.
Mechanical Instruments:
Along with questionnaires, researchers use mechanical instruments like mini tracking devices to record what consumers are watching on TV, phone’ GPS to track consumer’ movements around, or check out scanners, or what they are buying.
Neuromarketing, this is the technique, which includes MRI or EEG to learn what is in the heads of consumers, what they think about their brand. It records consumer involvement and emotional responses second by second. Its results are difficult to interpret, it is used in the combination with other approaches to get complete and clear picture of what goes on insides consumer’ head.
Implementing the Research:
Next step is to put marketing plan into action. It involves collecting data, processing it and analyzing the information. Research can be conducted by company’ internal researchers or by outside firms.
Researchers should watch carefully, whether the plan is implemented in the right way. They should also watch for problems in data gathering techniques and technologies, timelines and data quality.
Researchers must also process and analyze the data to isolate the important information and insights. Strict measures should be taken for accuracy and completeness and code them for analysis.
In the end of this step, researchers then tabulate the results and compute statistical measures.
Interpreting and Reporting the Findings:
Now the marketers should interpret the results, draw conclusions and present it to management. researchers should not manipulate the results and should present the clear picture specially the important findings and insights which are required to make major decision.
Managers should also give their time and make their own interpretations. As researchers are often at conducting research, and sometime they cannot interpret the findings. Best research goes vein if manager blindly accept the faulty interpretations, or managers may be biased and they accept the results that they wanted.
So, managers and researcher must work together closely while interpreting research results. Both must share responsibility for honest research process and resulting decisions.
Research Approaches:
Research approaches to collect primary data includes observation, surveys and experiments. Let’s discuss each;
Observational Research:
It is to gather primary data (exploratory research) by observing relevant people, actions and situations. Researchers use to observe consumer behavior, it provides more customer insights rather than questioning them. Marketers not only observe consumer behavior but they listen them carefully what they are saying as well, they can listen customers from social media, blogs or websites.
· Ethnographic: It is a process, in which, companies send observers to watch and interact with consumers in their natural environment. These observers are highly trained, they may be anthropologists and psychologists or company’ own researchers and managers.
Observational and ethnographic research provides kind of details that cannot be emerged from traditional research questionnaires.
Observational approach has its limitations as well, like attitudes, motives and private behavior cannot be observed. Then observation is not easy to interpret into word or while compiling a report. So, researchers use observation along with other data collection methods.
Survey Research:
The widely used method for gathering primary data, this approach is also best suitable to obtain the descriptive information. Surveys are conducted when companies want to know about people’ attitudes, knowledge, preferences or their buying behavior, these are better found out by asking them directly.
Surveys are widely used due to its flexibility nature. It is used to obtain different kinds of information in different situations. Surveys can answer all the marketing questions or decisions can be made on phone.
Surveys have its limitations and problems,
· Sometimes people don’t often remember things which are asked in surveys.
· Sometimes people are not willing to answer the questions, or consider things as private.
· People often answer wrong, answer even when they don’t understand the question, just to pose themselves as smarter.
· Some people often avoid to answer due to their busy routine.
Experimental Research:
Experimental research is best suitable to gather casual information. Experiments involve selecting alike groups of subjects, giving them different treatments, controlling unrelated factors and checking for differences in group responses. We can say, experimental research tries to explain cause-and-effect relationships.
· Example: A fast food brand may use experiments to test the effect on sales of two different prices before adding a new sandwich in the menu. It can introduce the same sandwich in different cities at different prices.
Contact Methods:
Information can be gathered by mail, by telephone, by personal interview or online. Each contact method has its strengths and weaknesses.
Mail Questionnaires: These questionnaires are used to gather large amount of information at lower cost per respondent.
Strength of mail questionnaires are, (i) big data is received, (ii) people often provide honest answers and (iii) chance of bias answers is very low.
Weaknesses of mail questionnaires are these surveys are not flexible as these are in similar structure and questions are same for all respondents, response rate is slow, takes longer time to complete,
Marketers are trying to shift to faster, flexible and lower cost email, online and mobile phone surveys.
Telephone Interviewing: Strengths: Through telephone surveys, information can be gathered quickly and are far more flexible than mail questionnaires. Interviewer can skip some question willingly explain difficult questions to respondents to get the accurate answers. Response rate is higher than mail questionnaires.
Weaknesses are, (i) cost per respondent is higher than mail questionnaires. (ii) Some people may don’t share their personal things with interviewers. (iii) element of biasness is there, (iv)
Most of the people don’t want to receive unknow or sales or marketing calls.
Personal Interviewing: It takes further two forms, individual interviews and group interviews.
· Individual Interviews are often taken in streets, offices, shopping malls etc. Interviewer can guide the interview after analyzing the situation. These interviews are flexible. Interviewers can show packages or products about which interview is conducted. Interviewer can explain questions to respondents. These individual interviews are often three to four times costly than telephone interviews.
· Focus Group Interviewing: Group interviewing is to invite small groups of people to meet with a trained moderator to talk about service, product or organization. Moderator encourage talk freely and easy discussions to get in return deeper feelings and thoughts of participants. Participants are often paid for their time. As the moderator “focusses” discussion, so the name is focus group interviewing.
It’s becoming major qualitative marketing research technique to get fresh customer insights. Moderators observe people’ conversational flows, body movements, hear their opinions and group interplays. They also listen from behind the one-way mirror, video recording for later study or video recording if sitting far-off locations.
Challenges are, people participating in focus groups are often not honest, they hid their real feelings. It is very hard to generalize from results as they employ very small samples to keep time and costs down.
To overcome these problems, researchers are trying to modify the focus group design. Some companies are designing in a way to make participants feel relaxed to get more authentic response.
Immersion Groups: these are smaller groups of consumers who directly interacts with product designers without any moderator.
Online Marketing Research:
Internet has great impact on how marketing research is conducted. Now researchers are gathering data through online marketing research i.e., online focus groups, internet and mobile surveys, experiments, consumer tracking and online panels and brand communities.
A company can use internet and smartphone for following purposes;
· Questionnaires can be made on website.
· Mobile phones can be used to invite people.
· Online panels can be made for regular feedback, live discussions, or online focus group,
· Online experiments (different prices, headlines, or product features)
· Testing new products by establishing virtual shopping environment.
· Learning consumer behavior by tracking their click streams.
· It is well suited for quantitative research.
Advantages:
· It is cost effective
· As well as it saves time, it is far quicker than traditional and old research methods.
· It can reach respondents quickly and gets their response instantly.
· Once the questionnaire is set-up, now the cost difference is very little for 10 respondents and 10,000 respondents.
· With the help of internet, now any smaller company can conduct research and make their surveys using different websites (www.snapsurveys.com or www.surveymonkey.com,)
· Through internet it is now easy for researchers to reach hard to reach consumers like office executives, busy house-wives, etc.
· Qualitative research can also be conducted by using filters while selecting participants.
Drawbacks:
· It is hard to know, who is on the other side. It is very difficult to know, who is answering the questions being asked.
Online Behavioral and Social Tracking and Targeting:
Here marketers and researchers listen and watch consumers by actively tracking the unsolicited and unstructured customer information already available on the internet. Traditional marketing research provides logical consumer response to structured and intrusive research questions where online listening provides the passion and unsolicited consumer opinions.
Tracking consumers may include;
· Scanning customer reviews and comments.
· Using online tools to sort and analyze big data of consumer brand-related comments and messages, which consumers share on social media sites or blogs.
· It provides valuable insights about what consumers are feeling and saying about the brand.
· It helps to develop positive brand experience and relationships.
· More and more companies are now setting up social media command centers to utilize internet to get customer insights.
Behavioral Targeting: it is to use consumer tracking data to target ads and offers to specific consumers.
Example: if you add Samsung mobile in your cart on some shopping website, and don’t buy it, and later if you are trolling some website, you may see the ad of Samsung mobile that you did add to cart but didn’t buy it.
· Behavioral targeting: it tracks consumer movements across online site.
· Social targeting: it mine individual online social connections and conversations from social networking sites. Example, while using Facebook, you may see the ad of a wallet that your friend has just bought from some other website.
Sampling Plan:
Marketing researchers study small samples of total consumer population to draw conclusions about large groups of consumers.
Samples: It is a segment of population selected for marketing research; it represents the population as a whole. Ideally, the sample should represent the whole population, so that researchers can make accurate estimates of the behavior and thoughts of larger population.
Designing a sample requires three decisions;
· Who: Who is to be studied?
· How many: how much should be the size of sample.
· How: how the people in the sample be chosen.
Following are the types of samples;
Probability Sample:
· Simple random sample: Every member of population has a known and equal chance of selection.
· Stratified random sample : In this population is divided into groups (in regards with age, occupation etc.) and random samples are taken from each segment.
· Cluster (area) Sample: The population is divided into mutually exclusive groups (such as blocks), and then drawing a sample of the groups to interview.
Nonprobability Sample:
· Convenience sample: Researcher choose the easiest member of population to obtain information.
· Judgment sample: researchers use their own judgment to choose members of population, who they think are good prospects for accurate information.
· Quota sample: the researcher finds and interviews a prescribed number of people in each of several categories.
Research Instruments:
Researchers use two main research instruments, i.e., Questionnaires and Mechanical Instruments to collect primary data.
Questionnaires:
Questionnaires are the most commonly used instrument, whether the research is conducted in person or by phone, by email or online. Questionnaires are very flexible. It includes questions, which may be open ended or closed ended.
Closed-ended questions include MCQs, it provides answers which are easy to interpret. And open-ended questions allow respondents to answer in their own words, Example; British Airways may ask travelers “what is your opinion about British Airways?”, it is mostly used in exploratory research to get the answers of “what people think”.
Instructions:
· Researchers should be careful in the use of wording and ordering of questions.
· They should use simple, unbiased and direct wording.
· Questions should be arranged in logical order.
· The first question should grab the interest of respondent and difficult or personal questions should be asked in the end.
Mechanical Instruments:
Along with questionnaires, researchers use mechanical instruments like mini tracking devices to record what consumers are watching on TV, phone’ GPS to track consumer’ movements around, or check out scanners, or what they are buying.
Neuromarketing, this is the technique, which includes MRI or EEG to learn what is in the heads of consumers, what they think about their brand. It records consumer involvement and emotional responses second by second. Its results are difficult to interpret, it is used in the combination with other approaches to get complete and clear picture of what goes on insides consumer’ head.
Implementing the Research:
Next step is to put marketing plan into action. It involves collecting data, processing it and analyzing the information. Research can be conducted by company’ internal researchers or by outside firms.
Researchers should watch carefully, whether the plan is implemented in the right way. They should also watch for problems in data gathering techniques and technologies, timelines and data quality.
Researchers must also process and analyze the data to isolate the important information and insights. Strict measures should be taken for accuracy and completeness and code them for analysis.
In the end of this step, researchers then tabulate the results and compute statistical measures.
Interpreting and Reporting the Findings:
Now the marketers should interpret the results, draw conclusions and present it to management. researchers should not manipulate the results and should present the clear picture specially the important findings and insights which are required to make major decision.
Managers should also give their time and make their own interpretations. As researchers are often at conducting research, and sometime they cannot interpret the findings. Best research goes vein if manager blindly accept the faulty interpretations, or managers may be biased and they accept the results that they wanted.
So, managers and researcher must work together closely while interpreting research results. Both must share responsibility for honest research process and resulting decisions.
Information which is gathered earlier form sources like, internal databases, competitive marketing intelligence and marketing research often requires further analysis before taking crucial decisions. This may include learning about the relationships within the sets of data, it might also involve the application of analytical models which helps them in decision making. Once the information is processed and analyzed it should be made available to right decision makers at the right time.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
This is the era of data, and how to manage the big data is a big problem in these days. Companies already have so much data, but still, they are gathering more and more customers related information from each touch points (customer purchases, service and support calls, sales force contacts, web and social media site visits, payments interactions, etc.).
CRM: manages the detailed information about individual customers and carefully manage customer touch points to maximize customer loyalty. CRMs can be taken from companies like Microsoft, Oracle, SAS or salesforce.com etc.
CRM software integrate customer and marketplace information from each source, analyze it, and apply the result to build stronger customer relationships. It contains everything that the company’ sales, service and marketing team knows. CRMs can be used to identify high-value customers, target them more effectively, cross sell them company products, and create customized offers to specific customer requirements.
Big Data and Marketing Analytics:
Simply gathering and storing big data has a very little value. marketers must mine the gems. A data expert says “right data trumps big data” and this is the job of marketing analytics.
Marketing analytics: it consists of analysis tools, technologies and processes by which marketers dig-out meaningful patterns in big data to gain customer insights and measure marketing performance.
Marketers apply marketing tools to big and complex data gathered from social media, mobile phone, web, and other big data sources. Benefits of CRMs and big data analytics don’t come without risks and costs. Just technology, or buying a costly software stand alone cannot do much, marketers must start with the fundamentals of managing customer relationships, and then employ high-tech data analytics solutions. It’s the relationship, that CRM is all about.
Distributing and Using Marketing Information:
Marketing information has no value if it is not used to make better decisions. So, marketing information should be readily available when needed to managers or to those who need it. It may be in the form of regular performance reports, intelligence updates or results of research studies.
Advanced CRM software helps managers to access the required information at anytime from anywhere. They can get reports, researches, information or anything they want. Thanks to technology, managers can access CRM from office, at home or sitting somewhere.
Some companies allow suppliers and customers to manage their accounts on their CRM. This creates customer and supplier satisfaction. It gives a sense of transparency, real time track record etc. in the end it builds stronger relationship, which is the need of time.
Here we will discuss marketing information in two special contexts, which
are marketing research in small business and nonprofit organizations and
international marketing research. Then later in this section we will take a
look at public policy and ethics issues in marketing research.
Marketing Research in Small Business and Nonprofit
Organizations:
Like big companies, smaller companies and nonprofit organizations also
need data market information to make better decisions. Due to lack of budget,
they cannot conduct carry out big researches or opt expensive information
sources but, they can use cheap or free research techniques.
They can spend time on internet, create focus groups, can interact with
customers and other stake holders to get the useful insights. Many associations
offer free publications, like www.sba.gov, bureau of economic
analysis etc., provide free information and advice about start-ups, financing
and expanding a small business.
Smaller firms can go for research techniques like secondary data, surveys
observations and small experiments are less costly but must be conducted with
care.
International Marketing Research:
International researchers face different problems than domestic
researchers. Domestic researchers deal in homogenous markets within a single
country, where international researchers deal with diverse markets in many
different countries. These markets vary greatly economically, culturally, their
customer and buying patterns.
In many countries, international researchers may find difficulty in
getting secondary data. It can be due to lack of facilities or cultural
differences. There are some big international research services operate in many
countries. Example: Nielsen Company has offices in more than 100
countries.
Because of scarcity of data companies can opt to go for Primary data
collection. It also has some problems, like developing good samples, in US
surveys can be conducted through phone calls, emails, or mails to construct samples.
But this may not work in many countries. Like there are 84 internet users per
100 people in US, in Mexico, its 43 users out of 100 and this number drops to 2
internet users per 100 people in Madagascar. If we talk about postal services,
in Brazil 30 percent of mails never delivered, in Russia mail delivery may take
weeks and, in many countries, due to poor road conditions and transportation
system there are area which are hard to reach. This makes interviewing people
difficult and expensive.
Cultures also pose many problems for many researchers, most
importantly language (also include idioms, phrases, and statement which vary in
their meaning) barrier. Researcher first develop the questions in English, then
translate them in respective languages and again the results will be translated
back in English. This increases cost and chances of error is there.
Attitudes and customs also vary country to country. In some countries
people show positive attitude towards surveys and researches but in other
countries people may not like to answer or talking to strangers.
Despite all of these problems, companies want to operate internationally
should conduct researches, even though these are little costly but to go global
blindly can cause more damage.
Public Policy and Ethics in Marketing Research:
Marketing research benefits both, companies and consumers. Through
successful marketing research companies get customer insights and make better
decisions and policies, in return they consumers get better services and
products, which stronger the relationships. But it causes ethical issues as
well, following are two public policies and ethical issues are intrusions on
consumer privacy and the misuse of research findings. Let’s discuss each;
Intrusions on Consumer Privacy:
Many consumers feel positive about marketing research, like to be
interviewed and believe that it serves a useful purpose. But many feel unsafe
and don’t want to share their opinions, don’t want to be interrupted, don’t
want to answer the questions and believe that companies are building huge data
bases and will use this information to manipulate their purchases.
Questions which are hard to answer:
·
Its good or bad to record customer demographics and shopping
behavior to serve them better.
·
Should we encourage or offend companies that monitor consumer
posts on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter or YouTube to be more responsive.
·
Should we worry, when companies use our mobile phone provide
location-based information, offers and ads?
Consumer Confusion:
Consumers are confused between personalization and privacy. They want to
receive relevant and personalized offers which should meet their needs, at the
same time they worry that companies may track them too closely.
Addressing Privacy Issues:
If companies fail to address privacy issues, they may lose consumer trust
and consumers become angry and increased government intervention. In this
regard, marketing research associations like “Your opinion counts” or
“respondent bills of rights” takes initiative of educating consumers about the
benefits of marketing research.
Recommendations:
·
Many big companies like IBM, Microsoft, Apple, Facebook etc.
hire chief privacy officers, whose job is to safeguard the privacy of
customers.
·
Offer consumers value in return of information. Like while
shopping on E-stores, they record previous purchase history and recommend
products to consumers in future accordingly.
·
The best approach is to ask only the required information.
Misuse of Research Findings:
Research findings can be powerful persuasion tool, many companies use
research findings in their advertisements and promotions.
In some cases, it appears that research surveys are designed to produce
the intended effect. Few advertisers rig their research designs or blatantly
misrepresent the findings. This rises the dispute over the validity,
interpretation and use of research findings. Almost every research can be
interpreted variously depending on the researchers’ viewpoint and bias.
Remedies:
Recognizing that marketing research can be manipulated and abused,
several associations like, American Marketing Association, the Marketing
Research Association and the Council of American Marketing Organization (CASRO)
have defined the codes of research ethics and standards of conduct. CASRO
outlines;
·
Researchers’ responsibilities to respondents, including
privacy, confidentiality and avoidance of harassment.
·
It also highlights major responsibilities in reporting
results to public and clients.
Other
than these above-mentioned recommendations, companies should take
responsibility for policing the conduct and reporting of its own marketing
research to protect consumers’ best interests as well as its own.