
Chapter Outline
- What’s your global Perspective?
- Understanding the global environment.
- Doing business globally.
- Managing in a global environment.
Managers may show 3 types of attitudes toward global businesses.
Ethnocentric attitude:
In this type managers have parochialistic belief; these are kind of beliefs in which people think themselves superior than others.
They think that they can better manage the tasks than the employees or managers in the host country.
They simply believe as “ours is better than others”
Polycentric attitude:
Managers having polycentric attitude believe that the managers or employees working in the host country are more compatible than ourselves.
They can make better decisions than us.
Geo-centric attitude:
People having this type of attitude have universal type of nature.
They respect talented people, without concerning, where are they from, what is their origin.
They look for best people from the world to get their work done.
Trade between countries and organizations isn’t new, it is happening from centuries.
3.2.1. Regional trading alliances:
There are 3 big regional trade alliances, these are, EU (European Union), NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement), ESEAN (Association of southeast Asian Nations).
EU (European Union):
· It is an economic and political union of 27 democratic European countries.
· It was formed in 1992, to make European countries stronger against US and Japan.
· After EU is formed, common barriers removed are related to travel, trade, employment, investment.
· Citizens of EU can work anywhere in EU countries and retire there.
· They introduced Euro Currency for trading purpose.
NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement):
· It was formed on 1st of Jan, 1994.
· It eliminated most tariff barriers to promote trade between US, Canada and Mexico.
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations):
· It was established on 8th of Aug, 1967 by five original members, those are Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
· It was formed to promote the economic growth, social progress and cultural development.
· It was also formed in order to bring stability, security and bring peace in the region.
Other trade alliances:
It includes:
AU (African Union): it includes 53 African nations
EAC (East African Community): it includes 5 East African Nations including Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania and Uganda.
SAARC (South Asian Association for regional cooperation): It includes 8 nation including Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal and Maldives.
3.2.2. Global trade mechanisms:
There are 4 global trade mechanisms, these mechanisms ensure the continuity of trade Efficiently and effectively.
These mechanisms are,
World Trade Organizations (WTO)
The international Monetary fund
World bank group.
Organization for economic cooperation and development.
§ World Trade Organizations (WTO):
WTO is a global organization of 153 nations.
It was formed after the end of World War II
It helps countries to conduct trade through a system of rules.
It plays important role in monitoring, promoting and protecting global trade.
Critics says it has destroyed jobs and natural environment.
§ The International Monetary
fund:
It is an organization of 185 countries.
It promotes international monitory co-operation.
It provides policy advice, temporary loans and technical assistance to maintain financial stability in the countries to make their economies stronger.
§ World bank group:
It is a group of five institutions which are owned by its members.
It also provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries.
They provide support for economic growth of country and for poverty reduction.
§ Organization for economic cooperation and development:
The former OECD was formed in 1947 to manage the American and Canadian aid for restructuring of Europe after World War II.
The recent OECD is Paris based.
Its mission is to help its 30 member countries, to achieve sustainability in economic growth by raising the living standard of its residents by maintaining financial stability.
When needed OECD do negotiations with OECD member countries to set the “rules of game”.
This organization have focus on combating small scale bribery related with overseas
commerce.
Having long experience in facilitation now OECD shares its experience with more 70 emerging markets.
Companies around the world do business globally, but the question is how they do it.
Different types of international organizations:
· Multinational corporation (MNC):
It is any company that operates in different countries.
· Multidomestic corporation:
It is a company that don’t limit the decision making to home country. But allow host countries to run business according to need.
They show polycentric attitude. E.g. Nestle.
· Global company:
This type of companies manages and make decisions from the home country,
This type of organizations has ethnocentric approach.
· Transactional, or borderless organization:
This type of companies makes such arrangement to eliminate geographic barriers.
They reflect geocentric attitude.
For example: Thomson SA is legally France based company, but it has eight major locations in the world. Their CEO said “we don’t want people to think we are based anyplace.”
Forms of globalization:
· Strategic alliances:
Partnerships between an organization and a foreign company, who share resources and knowledge to make a new product or service.
· Joint venture:
it is a type of strategic alliance in which partners agree to form a new separate and independent organization for business purpose.
· Foreign subsidiary:
This term refers towards direct investing in a foreign country to set up a separate and independent office.
Managing in another country is different
and challenging than in the home country.
3.4.1. The
political/legal environment:
Political and legal environment
is not stable in every country.
For example,
in Pakistan environment in this context is just not stable, it is too
uncertain, anything can happen anytime.
So keeping
this thing in mind, managing a company in Pakistan is very challenging for a
foreign manager.
Political
and legal environment is very much stable in US.
3.4.2. The
economic environment:
A global
manager must be aware of economic conditions while working in other countries.
There are two
types of economies, they are, free market economy and planned economy.
·
Free market economy:
A free market
economy is where resources are primarily owned and controlled by private
sector.
·
Planned economy:
It is a type
of economy in which economic decisions are controlled by central government.
A country’s
economy is neither pure free nor planned. They both intervene and show some
influence.
Other factors
which a manager should keep in mind are currency exchange rates, tax policies
and rate of inflation.
3.4.3 Cultural
environment:
Culture varies country to country, even in a county from region to
region.
So, managing
and collaborating with people from different cultural background is not that
much easy.
National culture:
Culture
shared by people of any country is its national culture. Values and attitudes
shape the behavior and beliefs of people about what is important.
It is easy
for someone to know the legal, political and economic environment, but to know
the culture of some other country isn’t so easy.
Hofstede’s framework for assessing cultures:
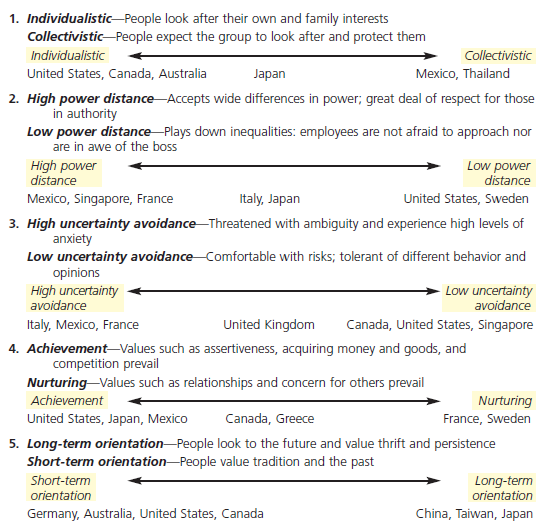
The GLOBE framework for assessing cultures:
The global leadership and organizational behavior effectiveness (GLOBE) extended the work done by Hofstede and apply research on 18000 people from 62 countries. Research found nine dimensions on which national culture differ.

Global management in today’s world:
· Challenge of openness:
It includes challenges like
i-Terrorism
ii-Economic interdependence of trading countries
iii-Cultural differences
· Challenges of managing a global workforce:
Ø Cultural intelligence:
i- Knowledge of culture that, how cultures vary from each other.
ii- Mindfulness: the ability to pay attention to signals and behaviors in different cultural situations.
iii- Behavioral skills: using knowledge to behave in different situations.
Ø Global mind-set:
i-intellectual capital: having knowledge about international businesses and capacity to learn how business work globally.
ii-psychological capital: allow your mind to accept new ideas and get new experience.
iii-social capital: ability to make relations and connections with other people who are different from you.