
Chapter Outline:
· The Microenvironment and Macroenvironment.
· The demographic and economic environments.
· The natural and technological environments.
· The political-social and cultural environments.
· Responding to the marketing environment.
Marketing environment:
These are forces and actors outside the marketing, which effects marketing management’ abilities to build and maintain successful relationships with target customers.
Marketing environment consists of microenvironment and macroenvironment, let’s look at each in detail.
Micro-Environment:
It includes actors which are close to company, and effects its ability to engage and serve its customers. These may be suppliers, customer markets, public, competitors and marketing intermediaries.
Marketing management’ job is to build strong relationships with customers by creating customer value and satisfaction. Marketing managers cannot do this alone, below mentioned figure shows, marketing managers need to build stronger relationships with company’ other departments to make up company’ value delivery network.
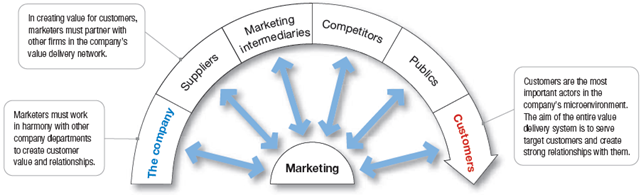
The Company:
While designing marketing
plans, marketing management need to collaborate with company’ other groups such
as, finance, purchase, manufacturing, accounting or R&D. All these
interrelated groups form internal environment.
Top management sets,
company’ vision, targets, objectives, broader strategies and policies.
Marketing managers take decisions within these broader plans and strategies.
With marketing taking lead, all departments share responsibility for understanding customer needs creating
value for customers.
Suppliers:
Suppliers play an
important role in company’ overall value delivery network, as they provide
resources to company to produce its goods and services. Marketing managers must
watch carefully supplier availability and costs.
Supply shortages, n delays
can damage sales in the short-term and customer satisfaction in the long-term.
If supplier rises the material cost, may force company to increase prices which
in result can harm company’ sales. Marketers today treat their suppliers as
partners in creating and delivering customer value.
Marketing Intermediaries:
Marketing intermediaries
are the firms, who help companies to promote, sell and distribute its products
to final customers or buyers. These are resellers, physical distribution firms,
marketing services agencies and financial intermediaries. Let’s discuss each;
·
Resellers: These are distribution channel firms, retailers and
distributers, who help companies to find customers or make sales for them.
·
Physical distribution firms: It helps the company with its
stock, and move its products from manufacturing site to different destinations.
·
Marketing services agencies: These are the firms, who help
companies to promote its products to right markets. These include advertising
agencies, marketing research firms, marketing consulting firms and media firms.
·
Financial intermediaries: these are firms who help companies
in financial transactions and insure against the risk associated with the
buying and selling of goods. These include banks, credit companies or insurance
companies etc.
With the growing need of
today, marketing managers work with these marketing intermediaries as partners
rather than taking them simply a channel to sell their products.
Competitors:
Marketing concept says
that a company should provide superior customer value and satisfaction to its
customers than its competitors. Marketing managers should always be eager to
take advantage of opportunities by positioning their offerings strongly against
competitor’ offerings in the minds of customers.
One strategy may not work
for all companies. Managers should design strategies according to their firm’
size, capacity and market situations around them.
Publics:
A public is any group, who
have actual or potential interest in or have impact on company’ ability to
attain targets. Publics can be classified into following seven types:
·
Financial Publics: This group effects company’ ability
to obtain funds. Major financial publics are banks, investment analysts or
stockholders etc.
·
Media Publics: media publics are television, newspapers, blogs,
magazines and other social media. This type of publics disperses information,
news, editorial opinions or other content.
·
Government Publics: these can affect companies
regarding product safety, truth in advertising and other matters.
·
Citizen-Action Publics: company’ public relations
department should always stay in touch with these consumer groups and maintain
good relationships with them. These citizen-action public groups are consumer
organizations, environmental groups, minority groups and others, these can
question company’ marketing decisions.
·
Internal Publics: this group include, company managers, workers,
volunteers and board of directors. Big companies use new letters to transmit
information to employees. When employees are happy with company policies, they
show positive attitude in their routine duties.
·
General Public: Companies should always be concerned about its image
in the minds of general public. General public’ attitude toward company’
products and services matter a lot. Public image of company effects buying
behavior of customers.
·
Local Public: This includes local communities and organizations.
Larger firms work for development of communities they operate in.
A company can design
marketing plans for both public and its consumers. Example: if company
wants to attract customers, build its image or generate a positive word of
mouth, for this companies need to make favorable offers to public.
Customers:
Customers are most
important actors in the company’ microenvironment. Whole marketing efforts
revolve around customers. The purpose of value delivery network is also to get
customers engaged and building strong relationships with them. There are five
types of customer markets, companies may target any or all of them, these
markets are;
·
Consumer Markets: These are individuals and households, who buy
products for personal consumption.
·
Business Markets: They buy products for further processing or use in
manufacturing process.
·
Reseller Markets: They buy products or services to resell at some
profit.
·
Government Markets: these are government agencies, who
buy products and services to produce public services, or transfer to the people
who need those products or services.
·
International markets: these are buyers in other
countries, including consumers, resellers, producers and governments.
Macro-Environment:
The macroenvironment
consists of larger societal forces who shape opportunities and pose threats to
the company. There are six forces, which includes, demographic, natural,
economic, political, technological and cultural forces.
Some forces are unforeseeable and
uncontrollable, where others can be predicted and controllable through skillful
management. For this companies need to adapt changes in the environment.
Companies, who don’t adapt change cannot face difficult times.
The Demographic Environment:
Demography is to study human population, regarding their age, size, location, density, race, gender, occupation and other statistics. The human population has grown to around 7.3 billion and is expected to grow to more than 8 billion by 2030. Marketer are interested in studying demographic environment as it is about humans an humans make markets.
Changes in demographic environment leave impact on business, so marketers need to keep an eye these changes occurring. They need to analyze changing age and family structure, geographic population shifts, educational characteristics and population diversity. Let’s discuss each;
The changing Age Structure of the Population:
The Baby Boomers | The babies who were born after World War II i.e., between 1946 to 1964. The wealthiest generation ever born in US. They are always open to new brands, they like brands who appeal their youthful thinking. |
Generation X | People born between 1965 – 1976. They are often overlooked, as they grown-up under the shadow of baby boomers. They are less materialistic, appreciate experience not acquisition. They are sensible buyers, research products before they buy, prefer quality rather than quantity. They never stop improving. |
Millennials or Generation Y | Born between 1977 and 2000. Facing higher unemployment and facing debts. They are huge in number and make big market for companies. They are grown up with modern technologies, i.e., computers, TVs, mobile phones |
Generation Z | People who are born after 2000. Some analysts include people born after 1995. They are shaping their brand experiences for their future. Highly comfortable with digital technologies, smartphones, wireless internet, highly mobile connected. They are the blend of online and offline world, as they socialize and shop.
|
Generational Marketing:
Do companies need to offer different products for each different segment?
To cater the needs of every segment is near to impossible for any brand. Tastes and needs vary of people of different age.
Marketers need to form more precise age-specific segments within each group (split baby boomers into three smaller groups, leading edge, core boomers and trailing-edge boomers) and then target any among them in the beginning, and after getting successful in one small group start targeting another group along with the existing one.
The Changing Family structure:
Family structure around the world has changed if we compare it with past. Earlier men used to work and earn the bread for their family. Family included parents, wife, children and sometimes grandparents as well.
Now things are changed enough, number of working women has increased greatly. They work in the industry shoulder to shoulder with men. Now women are more independent. Now more people are divorcing or separating, choosing not to marry, remarrying or marrying without intentions of having children.
Marketers must keep these changing factors in mind while making strategies, because each person have different needs and buying habits.
Geographic Shifts in Population:
It is what we say migration from one country to another or within countries. Earlier people use to migrate from villages or smaller towns to big cities in search of jobs.
And now people are shifting to microcities, small cities located beyond congested metropolitan areas. These areas have restaurants, shopping centers, community organizations but without pollution, traffic jams, high crime rates, high property taxes which are associated with metropolitan cities. This has promoted SOHO (small office/home office) concept.
Marketers taking it as an opportunity and providing them software (Cisco’ Webex) for “work from home”. Or providing them shared work spaces on rent. Etc.
A Better-Educated, More White-Collar, More Professional Population:
People are getting more degree holders in comparison with earlier times. Now we find so many Master’ degree holders around us. Now people look for white collar jobs. There is a lot of growth for skillful professionals.
This rise in number of educated people have greatly affected the buy behavior of people.
Increasing Diversity:
Countries or markets are getting more and more diverse. Countries vary in their ethnic and racial makeup. People move from one place to another caries his culture and norms with him.
Marketers now face increasingly diverse markets at home and abroad. Big companies like, P&G, McDonald’ design products for different people. McDonald’ offer burgers and other products with Halal ingredients in it for Muslims in different countries.
Companies are also targeting Lesbians, Gay, Bisexual or transgender (LGBT) by featuring them in their marketing campaigns.
Companies are also considering adults with disabilities. Most companies have vacant positions in their offices which are for disabled persons. Then companies are featuring them in their advertisements as well. Example: Nippon Paints TV commercial featured a girl who cannot see.
Marketers are now diversifying their marketing efforts to take the advantage of opportunities in fast growing segments.
The Economic Environment:
The economic environment consists of economic factors that affect consumer purchasing power and spending priorities. Economic factors sometimes effects dramatically on consumer’ spending and buying behavior.
Example: People in Pakistan could buy Apple’ iPhone, but in recent times (2021-2022) facing worst economic times, most of the people don’t afford to buy it. People are shifting to economic cars. Etc.
Marketers in challenging economic environment offer the right combination of product quality and good services at a fair price, because in such situations, people set their priorities and spend sensibly.
Slogans like “Pay less, Expect more”
Changes in economic factors like income, interest rates, savings and cost of living effects greatly the buying priorities of consumers. Rich become richer but poor remains poor. This makes market tiered.
Companies watch these variables by careful forecasting. With adequate warning companies can survive and even can take advantage of changes in economic environment.
The Natural Environment:
The natural environment includes physical environment and natural resources which can affect the company’ marketing strategies.
Example: extreme weather conditions, shortage of raw materials or natural disasters etc.
Obviously, companies cannot prevent these natural events but they can forecast them and prepare themselves for such disastrous events.
Example: Courier service FedEx have meteorologists in their staff, who regularly anticipate weather conditions. This keeps FedEx updated about recent or coming weather conditions. It is necessary because, if a person need a parcel in Canada, he don’t care about the weather conditions in England.
Environmental Trends:
· Shortages of raw material: it may include, renewable resources like forests and food etc., or nonrenewable resources like oil, gas coal etc. every resource need to be used wisely as it is becoming scarce.
· Increased Pollution: industry always damages the natural environment of surrounding areas. Example: industries cause air pollutions, road damages, dust pollutions, use resources of surroundings, waste disposals or chemical pollutants etc.
· Increased Government intervention: many countries have made strict rules about pollution, and companies have to follow these rules at any cost. Rich countries can implement strict policies in the industries but poorer countries cannot due to shortage of funds or political will. America formed Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 1970.
Many big companies are now working for the betterment of Environment Sustainability. It can be done through many means, for Example, companies make packaging material which is recyclable or biodegradable. It is now in the mission of many companies, not to harm the environment.
The Technological Environment:
We see technological wonders like antibiotics, internet, smartphones or robotics surgery. Technology has made our lives so fast. I remember we used to save our date in floppy disks with very limited space of around 1 MB, then memory cards and USBs. Now big data of 1 or 2 TBs can easily be stored in inch sized USBs. This is a kind of dramatic force which is shaping our destiny.
It has given us both the blessings (automobiles, TV, Video calling with the loved one sitting thousand miles away, internet etc.) as well as horrors (atomic bomb, missiles, guns etc.). our attitude towards technology depends upon, whether we are impressed by its wonders or blunders. Marketers need to be aware of new technologies available in the market.
Example: Walmart make sure to apply RFID (radio-frequency identification) to track the products from Suppliers to distributers to customers. This a positive use of technology.
The Political and Social Environment:
Political environment includes laws, government agencies and pressure groups that influence or limit various organizations and individuals in society.
Legislation Regulating Business:
Even the people who strongly advocate the free-market economies believe that the system works well with at least some regulations. Government makes Public Policies, public policies are sets of laws and regulations, which limit businesses for the good of society as whole. Marketing activities are often under the strict influence of laws and restrictions country to country.
Laws cover the issues like competition, environmental protection, fair-trade practices, product safety, truth in advertisement, product safety, consumer privacy, pricing, packaging and labeling and other important areas.
These rules, laws and regulations change time to time, so, marketers need to be aware of these changes and prepare marketing strategies accordingly.
Business legislations addresses following major reasons.
· First is to Protect Companies from each other.
· Second purpose is to Protect Consumers. (Misleading consumers through advertisement or deceiving them through pricing and packaging)
· Third big reason is to Protect the Interests of Society.
International marketers have to follow so many strict rules and protocols to make sales internationally. New laws and enforcements will continue to raise. So, marketers need to watch these developments while planning their products and marketing programs.
Following are some rule and regulations:

Increased Emphasis on Ethics and Socially Responsible Actions:
It is to go beyond written laws and regulations; businesses are also governed by social codes and rules of professional ethics.
Socially responsible behavior: well reputed and enlightened companies encourage their managers to go beyond rules and regulations with a simple belief “do the right thing.” Such companies always seek opportunities to protect the long-run interests of their consumers and environment.
Online social platforms have raised new ethical concerns. Critics are worried about online privacy issues. Users themselves provide all their personal data to different websites. Which can cause problems for them in future. Even legitimate businesses collect and analyze consumer’ data to track his buying behavior. Critics are concerned that they have got so much data to take unfair advantage of consumers.
Cause-Related Marketing:
Many companies are now linking themselves with some good cause. They may take the concept of “Buy 1 Give 1” (for details of this model, go to menu tab – research articles – buy 1 Give 1 model) model, or by spreading messages among customers for the well-being of society or to educate them.
Example: the campaign “it can wait” run by T-Mobile. It was made to make people aware of how dangerous it can be to text while driving.

Example: Warby Parker, the online marketer of low-priced prescription eyewear. Company says “eyewear with a purpose” for every pair of glasses Warby Parker sells, it distributes a free pair to someone in need.
Critics worry that companies may use this technique to raise their sales. But if handled and managed well cause-related marketing can greatly benefit both the company and the cause.
The Cultural Environment:
Humans are social animals; they live particular societies. Every society have its norms which shape individuals’ perceptions, beliefs and values.
Cultural environment consists of institutions and other forces that affects society’ perception, basic values, preferences and behaviors. Following are cultural characteristics can affect marketing decision.
The Persistence of Cultural Values:
People in a particular society hold many beliefs and values, can be termed as core beliefs and secondary beliefs.
Core Beliefs: These are beliefs which are often passed on from parents and are reinforced by schools, religious institution, businesses and government. These beliefs and values are highly persistent and hard to change. Example. Believing in marriage, is a core belief.
Secondary Beliefs and values: these are often open to change. So, marketers can take chances in this case. Example: “Marrying in early life” is a secondary belief.
Shifts in Secondary Cultural Values:
Marketers always try to predict cultural shifts to identify new opportunities or threats. The major cultural values of society are expressed in people’ views of themselves and others as well as views of organizations, nature, society and universe. Let’s discuss each in short details;
People’ Views of Themselves: People vary in views about themselves, some want fun, want to enjoy, open to change, seek personal pleasure and escape while others strive for recreation, self-realization through religion, or career focused or other life goals. Some people see themselves as sharers and joiners while others are individualistic, some people like sophisticated look while others prefer to stay casual.
People buy such brands and services which match their views of themselves. So, marketers can position their brands to appeal to specific self-view segment.
People’ Views of Others: People’ views about others change over time. We are living in digital era. Some critics say, digital age will result in diminished human interaction. While trend watchers call it as the era of “Mass Mingling”, as more people interact, communicate, socialize, text will eventually result in real meet-ups and followers in the real world.
The other view says, in this world of digital socializing, people are together but are “alone together”, as they are sitting with friends, texting someone else, watching their own small screens etc.
Consumers continuously tap digital friends’ networks and online brand communities to learn about new trends in the market, what to buy, where to buy from and share brand experiences as well. So, marketers need to participate in these two networks as well.
People’ Views of Organizations: People vary in views and attitude towards organizations, corporations, government agencies universities or trade unions etc. People want to work with big companies and in return, they want them to work for the good of society.
In the past decade companies have loose employees’ trust and loyalty, it may be due to job insecurity, economic situations, greed from both sides, downsizing, poor HR employee policies etc.
This trend suggests that organizations need to review their policies and find new ways to win consumers and employee confidence.
People’ Views of Society: people also vary in their attitudes towards societies. Patriots defend it (prefer local brands), reformers want to bring change in it and malcontent want to leave it. People’ views about society effect consumption patterns and attitudes towards marketplace.
People’ Views of Nature: People vary in their views of nature, some feel ruled by it, others feel in harmony with it and some want to master it. From so many decades, humans are making experiments on nature, in recent times people has recognized that nature in infinite and it can be destroyed or spoiled by human activities.
Now people are shifting back to organic, natural and nutritional products, from fueling cars to alternative medicines and food items.
People’ Views of Universe: last, people’ views about origin of universe and their place in it. Some are already religious, some are atheists, some atheists converting religious and some religious people converting atheists and some being atheists are becoming spiritual, knowing themselves, nature and the purpose of universe etc.
These changing views affect their choices from TV serials, to books and other buying behaviors towards products and services.
It is said that, there are three types of companies, first are those who make things happen, second are those who watch things happen and third are those who wonder what’ happened.
Some companies view marketing environment as uncontrollable, to which they must adapt and react. They make strategies to avoid threats and take opportunities in the marketing environment.
Other companies take proactive approach towards the marketing environment. These firms make strategies to change the marketing environment. They adopt more aggressive actions to affect publics and forces in the marketing environment. Example: Apple’ iPod and iPhone, google search engine and Amazon’ online marketplace.
They hire lobbyists to influence legislation effecting their industry, stage media to get maximum coverage, run blogs on social media to shape public opinion, they file complaints with regulators to keep competitors in line and they make formal contracts to better control distribution channels.
Marketing management cannot always control environmental forces. But whenever possible smart marketing managers take a proactive rather than reactive approach to the marketing environment.