Chapter Outline:
· Company-wide strategic planning: Defining Marketing’ role.
· Designing the Business Portfolio.
· Planning Marketing: Partnering to build Customer Relationships.
· Marketing Strategy and Marketing Mix.
· Managing the Marketing Effort & Marketing Return on Investment.
Every company must prepare a survival and growth plan which fits right with the situation, opportunities, objectives and resources.
· Strategic Planning: It is the process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’ goals, capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities.
Companies usually make annual plans, long-range plans and strategic plans. Annual and long-range plans focus on current businesses and how to keep them going while strategic plans guide companies how to take advantage of opportunities in the continuous changing environment.
At corporate level, strategic planning starts by defining mission and purpose of company. After defining broader mission, companies develop tiny objectives, which further guides the company.
Next headquarter defines what business portfolio and product is best for the company and how much support will be provided to each one.
Keeping all these plans in mind, companies then develop marketing and departmental plans, which supports company-wide plan. So, marketing planning happens at business units, product and market level.

Defining a Market-Oriented Mission:
An impressive mission includes following questions, which are, what is our business? who is the customer? what should our business be? and what do customer value?
These questions look very simple, in-fact most of the companies fail to answer these simple questions. Successful companies continuously raise these questions and answer them carefully and completely.
Mission Statement:
A mission statement is a statement of organization’ purpose, what is wants to accomplish in the larger environment. A clear mission statement acts as an “invisible hand” which guides people in the organization.
Some companies make mission statement that revolves around their product or technology. For example: “we are chemical processing firm” or “we make and sell furniture”. As products and technology eventually becomes outdated so, mission statement should be market oriented. For Example: Microsoft’ mission statement is “empower every person and every organization on the planet to achieve more.”

Setting Company Objectives and Goals:
Companies need to split their broad mission into smaller objectives and goals. Manager of each department should be given an objective to accomplish, what comes may. Companies should design marketing strategies and programs to support marketing objectives.
After developing company’ mission statement and objectives, management should now plan its business portfolio.
· Business Portfolio: is the one that best fits the company’ strengths and weakness to opportunities in the environment.
Business portfolio planning involves two steps, first, analyzing company’ current business portfolio and second is to shape future portfolio. Following are the details of these two steps.
Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio:
The important and major activity in strategic planning is Portfolio Analysis, here company will carefully analyze the business and its products. Companies want to put strong resources into profitable businesses and phase down or drop its non-profitable businesses.
Management first identifies the key business units of the company, which are called as Strategic Business Units, these can be a company division, a product line or a product or brand. Then company analyzes that, which SBU needs how much support. Its good for companies to add and support products and businesses, which best fits with company’ philosophy.
Its purpose is to find ways, how companies can best utilize its strengths. For this purpose, SBUs are analyze on two important dimensions;
· 1st is, the attractiveness of SBU in the market and industry.
· 2nd is, the strength of SBU’s position in the market and industry.
Boston presented the best-known Portfolio-planning Method.
The Boston-Consulting Group Approach:
By using BCG Matrix, companies classify all its SBUs (Strategic business units) in accordance with Growth-Share Matrix.
On the vertical axis, there is Market Growth Rate, which depicts market attractiveness and on the horizontal axis Relative Market Share, is a measure of company’ strength in the market.

Stars: Stars are high growth and high share products or businesses. These businesses need heavy investments for their rapid growth. One day their growth will be slowed down and they will turn to cash cows.
Cash Cows: These are established businesses or products with low growth but high share in the market. These SBUs need very little investment to maintain its market share. Cash cows produces enough cash to pay bills and support other SBUs which need investments.
Question Marks: these are low share business units in a high growth market. These kind of SBUs need a lot of cash or investment to grab the market share. Managers need to think hard whether to invest in a question mark to make it a star or simply discontinue it.
Dogs: these are low growth, low share businesses and products. They may generate enough cash to maintain themselves. But don’t promise long-term sustainability.
As time passes, SBUs change their position in the growth-share matrix. Companies need to add new products and businesses in the portfolio, so that, one day they will become stars and then cash cows to finance other SBUs.
Companies must decide, what role each SBU will play in future. It can adopt one of the following four strategies, which are:
· Build: It is to invest more in a SBU to build it and make it a star.
· Hold: Tt is to invest little just to hold the market share.
· Harvest: It is milking short-term cash cow rather than waiting for long-term reward.
· Divest: It is to shut the project by selling it or using its resources for other projects.
Problems with Matrix Approaches:
These approaches have some following limitations:
· They can be time consuming, difficult and costly to implement.
· Management may find it difficult to define SBU and measure its growth and market share.
· These approaches focus on classifying current businesses and provide little advice for future planning.
· Rather than former strategic planning efforts, now it has gone more decentralized. Companies are handing over these responsibilities to cross functional teams, who are close to markets and have rich knowledge about customers.
Developing Strategies for Growth and Downsizing:
Designing business portfolio involves hunting new products and businesses for future. Every company needs growth, if it wants to compete effectively, satisfy their stakeholders and attract top talent. At the same time, companies need to be careful about, company; main objective is to manage profitable growth.
Following mentioned in the picture is a useful device for identifying growth opportunities;
Product Market Expansion Grid:
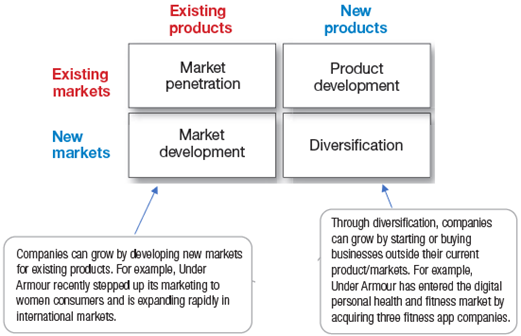
Market Penetration:
It is to make more sales of the current product line and in the existing market by bringing improvements in its marketing mix, i.e., product variations (style, color, etc.), advertising, pricing (offering discounts, etc.) and distribution (direct distribution to consumers, etc.)
Market Development:
Next is market development through identifying and developing new markets for its current product. For example: a clothing firm may now target females along with existing male customers. Expanding from domestic markets to international markets.
Product Development:
It is to offer more customized or new products in the existing markets, for example: a clothing firm may add perfumes range along with clothes.
Example: Uni-worth in Pakistan has added perfumes along with outfits.
Diversification:
It is to start new business or buying a company of product out of its current product line.
For example: Engro Pakistan, is in foods industry, have chemical plants, fertilizers etc.
Companies must also be prepared for Downsizing; it can be due to several reasons. It can be to lack of experience, non-profitable products, economic conditions, company’ internal changes etc.
Example: GM (General Motors) has pruned some underperforming brands from its portfolio, including Oldsmobile, Saturn, Pontiac, Hummer etc.
Customer engagement and value are the important ingredients in marketing’
formula for success. Marketing alone cannot do it alone, it partners with other
departments and working units to create an external value delivery network that
jointly serves customers.
Marketing plays important role in company’ strategic planning in numerous
ways.
·
First: it provides a guiding Philosophy, that is,
the marketing concept that revolves around creating customer value and building
profitable relationship with important consumer groups.
·
Second: marketing provides important Input to
strategic planners, by helping them to identify attractive opportunities in the
market and assessing whether, company have potential to take advantage from the
opportunity or not.
·
Third: marketing designs Strategies for individual
units’ objectives, after setting objectives, marketing’ responsibility is to
carry them out profitably.
Partnering with Other Company Departments:
Every department in a company is an important link in company’ internal Value
Chain. Each department plays part through value-creating activities to
design, produce, market, deliver and support the firm’ products. For this
companies needs to maintain and grow healthy coordination among different
departments.
Ideally, there should be harmony among different departments of company
to produce a value for customers. But in reality, there are so many conflicts
and misunderstandings. Marketing department demands extra effort from other
departments to provide better customer services, which cause disruption in
other department’ work and procedures i.e., purchasing costs, budget headaches,
increase inventory, etc.
Marketers need to find ways, and made each employee to “think consumer”. We
are in an era where, to engage consumers requires complete commitment from the
entire company “We are all marketers now.”
Partnering with Others in the Marketing System:
Companies need to build and grow relationships with suppliers,
distributors to engage and create value for customer and to improve Value Delivery
Network.
Value Delivery Network: A network which consists of
company, suppliers, distributors and ultimately customers, who collaborate with
each other to improve the performance of the entire system in delivery customer
value.
Example: Ford’ performance depends upon overall delivery network verses Toyota’.
Even, Ford manufactures best cars but it will lose market share, if dealer
network provides best customer satisfying sales and service experience.
Below mention picture shows marketing role, which summarizes the major activities involved in managing a customer-driven marketing strategy and marketing mix.
Through Marketing Strategy companies hope to create value for customers and achieve profitable relationships.

Let’s discuss each in details.
Customer Value-Driven Marketing Strategy:
Today, market is getting more and more competitive. So, in order to compete companies, need to be customer centered. Companies should always try to know customer’ needs and wants. They need to win customers and then engage and grow them by delivering superior value. Sound marketing requires careful customer analysis.
It is obvious that, companies cannot serve all customers, as they vary in their needs. There are companies who perform better than others in a particular segment. So, companies should divide markets into smaller segments and then prepare strategies for those chosen segments. This process involves market segmentation, market targeting, differentiation, and positioning, let’s discuss each briefly;
Market Segmentation:
Market segmentation is a process of dividing market into smaller distinct groups of customers who have different characteristics, needs or behaviors and who may require separate marketing strategies or mixes.
A market consists of various types of consumers, needs and products, a marketer must find out, which segment offer the best opportunities. Consumers can be distinguished on the basis of behavioral, geographic, demographic and psychographic factors.
· Market Segment: A market segment consists of consumer who show similar behavior and respond in a similar way to given set of marketing efforts.
Example: Suzuki offers different cars brand for different segments of consumers. Alto, Cultus, Ciaz etc.
Market Targeting:
After the company has carefully identified market segment, now its time to market targeting. Market targeting involves evaluating attractiveness of each market segment and then selecting one or two to enter.
Companies should consider such segment which can earn them profit and generate greater customer value and can sustain it for longer period of time. Companies may target one or more segments or may target a market niche depending on the resources they have.
Example:
Nike, introduced innovative running shoes for serious runners (market niche). Later after success, Nike started targeting other segments of market. Now it offers broad range of sports apparels and equipment. The secret behind its success in each segment is that, it designs different products to meet the special needs of each segment it serves.
Market Differentiation and Positioning:
After selecting target market, now it’s time to determine, what place they want in the segment and how to differentiate their market offerings to compete in the market.
· Positioning: It is the image of product or service in the minds of consumers. And obviously every marketer wants unique position in the minds of consumers for their products. So, for this, markets design special plans to distinguish their product from competitors to get greater advantage in the market. Example: Coca-Cola wants you to “Taste the feeling”, Pepsi says “Live for now”
· Differentiation: it is to differentiate market offering to create superior customer value. It can be done through innovation in the product, lower prices, excellent customer services etc.
The company’ entire marketing program should support the chosen positioning strategy.
Developing an Integrated Marketing Mix:
Marketing mix is a set of tactical tools that the firm use to get the response it wants in the target market. It consists of everything that a firm can do to engage consumers and deliver customer value.
The famous four Ps are, Product, Price Place and Promotion. Let’s discuss each briefly;

· Product: It is a goods-services combination, that a company offers to the target market.
· Price: the amount of money, customer will pay to get the product.
· Place: it involves company’ activities to make the product available for the consumers in the market.
· Promotion: these are the activities performed by companies to inform customers about their products.
Critics says, this marketing mix tool just focus on products, where are services? Like banking or airline services etc. The answer is, these are products too, and can be termed as service products.
There is another concern, four Ps takes the seller concern, as the market dynamics are changing, for this buyer’ viewpoint is also important. These can be better understood through four As, which are:

· Acceptability: to which extent, product exceeds customer expectations.
· Affordability: whether consumers are willing or are able to pay for the product.
· Accessibility: do the product is available in the market to customers or not.
· Awareness: the extent to which consumers and customers are informed about the product.
Four As relate closely to traditional four Ps, how;
· Product design influences its acceptability.
· Price effects affordability.
· Place to accessibility.
· And promotion to awareness.
Marketer’s effectiveness will be enhanced if they start process through four As and then build four Ps.
Managing Marketing Effort:

Managing the marketing involves five marketing management functions as shown in the picture.
First, company designs larger Plan and then translate into marketing and other plans for product, brand and division.
Then comes Implementation and Organizing, through this function company turns plans into actions.
Control measures and evaluates the result of marketing activities and taking corrective measures where needed.
Marketing Analysis:
Managing marketing function starts with complete analysis of company’ current situation. That can be done through SWOT (Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) analysis.

· Strengths: it includes company’ internal strengths, capabilities, resources and other situational factors that may benefit company in one way or other.
· Weaknesses: weaknesses are company’ internal limitations and negative situational factors which may harm company in way or other.
· Opportunities: these are favorable trends or factors in the external environment, to which companies may exploit to take advantage from.
· Threats: these are unfavorable trends or factors which are present challenges to performance of company.
The goal of SWOT analysis is to match the company’ strengths to attractive opportunities present in the external environment. Secondly, eliminating or overcoming weaknesses and minimizing the threats.
Marketing analysis provide inputs to every other marketing management function.
Marketing Planning:
Through strategic planning company decides what it wants to do with each business unit. Where marketing planning is to choose marketing strategy which will help the company to achieve its overall strategic objectives. A detailed marketing plan is needed for each business, brand or product. Below mentioned is a detailed marketing plan.
Content of Marketing Mix:

Marketing strategy includes specific strategies for target markets, the marketing mix, positioning, and marketing expenditure levels. It tells, how company will engage target customers and create value to earn value in return, how each strategy will respond to opportunities, threats and critical issues. Additional section plans action program to implement the marketing strategy along with the detailed supporting of marketing budget. Last section describes about controls which will monitor the progress, measure return on marketing investment and take corrective measures.
Marketing Implementation:
A competitive and brilliant marketing plan counts for none, if company fails to implement it successfully. Marketing implementation is to turn marketing plans into marketing actions to achieve strategic marketing objectives.
Marketing plan tells what and why of marketing activities whereas, marketing implementation talks about who, where, when and how.
Two firms may have same strategies, but one wins in the marketplace through faster or better execution. No doubt, marketing strategies often look easy but implementation is difficult.
People at all levels of marketing system need to work together to implement marketing strategies. While taking decisions about target segments, product development, branding, promotion and distribution company’ marketing managers need to consult with engineers about product design, with manufacturing unit about production and inventory related matters, with finance for funding and cash flow, outside the company with ad agencies for campaigns etc.
Marketing Department Organization:
Companies should design marketing organization, which will prepare marketing strategies and plans.
In smaller companies, there is often one person who do all the research, advertising, selling, customer service and other marketing work. With the passage of time, when company grows, a marketing department emerges for marketing activities.
In big firms, this marketing department have many specialists, product and market managers, salespeople, sales managers, advertising and social media experts and market researchers. So, to lead and head this much large marketing organization, companies have introduced a Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) position. This person takes up marketing related things on equal level with C-level executives like CFO (chief financial officer) or COO (chief operating officer) etc.
Example: British Airways, has named this position as Director of Customer Experience.
Modern marketing departments can be arranged in many ways,
· Most common one is functional organization, in which marketing activities are headed by, functional specialists, advertising mangers, sales manager, customer services manager, new product manager or marketing research manager.
· A company who operates inside the country and internationally have designed Geographic Organizations. In this, companies assign sales and marketing people to specific countries, districts and regions.
· Product Management Organization: Companies who sells different products and brands.
· Market and Customer Management Organization: when companies sell one product line to different markets and customer with different needs and preferences.
· Combination: companies that produces many products and serves different geographic and customer markets use the combination of functional, geographic and market organization forms.
Companies are now shifting their brand management focus towards customer management. They now think about managing portfolios of customers rather than managing portfolios of brands. Putting all the efforts to improve managing customer-brand engagement, experience and relationships.
Marketing Control:
It is to measure and evaluate the results of marketing strategies and plans and to take corrective actions to ensure that objectives are achieved. It includes four steps, which are:
· First, management sets specific marketing targets.
· Second, measuring performance in the marketplace.
· Third, evaluating the causes of any differences between expected and actual performance.
· Fourth, management takes corrective measures to close the gap between goals and performance. This may require changing action programs or even changing the goal.
Operating Control: it is to compare ongoing performance against annual plan and taking corrective action where required.
Strategic control: it is to regularly looking at marketing strategies are well matched with its opportunities, due to occurrence of rapid changes in the market company’ marketing strategies and programs quickly become outdated.
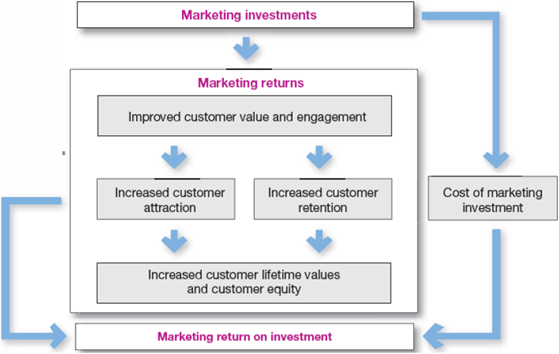
Measuring and Managing Marketing Return on Investment:
Marketing manager must ensure that company’ investment on marketing is well spent. In past, marketers spent big and marketing campaigns without thinking carefully about its productive returns. Their aim was to build brands and consumer preferences.
But now marketers are accountable for their spendings on marketing and their returns.
Marketing ROI: it is net return from marketing investment divided by the costs of marketing investments. This formula serves to measure the profits generated by investments in marketing activities.
ROI can be measured in terms of standard marketing performance such as brand awareness, sales or market share.
Marketing dashboard: it is the meaningful set of marketing performance measures in a single display used to monitor strategic marketing performance.
Furthermore, marketers using customer centric measures of marketing impact, such as customer engagement, customer acquisition, customer retention, customer lifetime value, customer experience and customer equity.
Below mentioned figure shows marketing investments and returns in the form of more profitable customer relationships. Marketing investments result in improved customer value, engagement and satisfaction which ultimately increases customer attraction and retention.