
Chapter Outline:
· What is marketing?
· Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs
· Designing a Customer Value-Driven Marketing Strategy and Plan.
· Managing Customer Relationships and Capturing customer value.
· The Changing Marketing Landscape.
Definition:
Marketing is engaging customers and managing profitable customer relationships.
In simple terms, there are two goals of marketing,
a) first is to attract new customers by promising better services and quality,
b) the second goal is to maintain and improve the relationship with existing customers by fulfilling the promises.
Examples:
Nike: Providing superior services to its customers by saying “just do it” and beating its competitors
Amazon: An online marketplace, attracting and maintaining worldwide customers by providing sense of Satisfaction with online purchases.
Today’ marketers adopt new techniques like websites, smartphone apps, online videos, blogs and social media along with the old techniques i-e. TV, magazines etc. to reach customers.
New techniques are more interactive and more customer focused.
Today’s marketers want to be the part of customers life and want to provide them enriched experience.
One advertisement that customer sees, there is a collective effort of technical team and marketers to grab customer’ attention.
Marketing Defined:
People think of marketing as just selling and advertisement, in-fact these are just the tips of iceberg.
In the new sense, marketing is to satisfying customer needs by providing them superior services.
Peter Drucker says “The aim of marketing is to make selling unnecessary”
What I have perceived from this definition is, to provide so much customer centric superior services that customer himself come to purchase your product.
“A set of marketing tools that work together to engage customers, satisfy customer needs and build customer relationships.”
Another definition is “the process by which companies engage customers, build strong customer relationships and create customer value in order to capture value from customers in return.”
The Marketing Process:
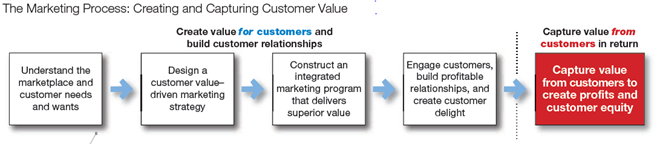
· The above figure shows marketing in a nutshell
· The five-step process forms the marketing framework.
· By creating value for customers, marketers capture value from customer in return.
In the first step, marketers need to examine the following five core concepts to understand customer needs, wants and the marketplace. i.e., i) customer needs wants and marketplace,
ii) Market offering, iii) Value and satisfaction, iv) Exchange and relationships, v) Markets.
Customer Needs, Wants, and Demands:
Needs:
Needs are states of felt deprivation.
Physical needs: for food, warmth and safety
Social needs: for belonging and affection.
Individual needs: for knowledge and self-expression.
Wants:
Wants are the form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality.
For example: an American needs food but want a Big Mac and fries.
Demands:
If wants are backed by buying power, wants become demands.
People want products and services with value added benefits and self-satisfaction.
Companies collect this data by analyzing customer’ buying habits.
Successful CEO’ follow the term “stay close to customers”
Market offerings (Products, Services and Experiences):
Market offerings are a mix of product, services, information or experience to market to satisfy the needs or wants.
Market offering is not limited to physical product, it also includes services, activities or benefits to satisfy customers.
Personalized messages are required, i.e., San Diego runs an advertisement “Happiness is calling” (city’ great weather, good times, bays and beaches, nightlife and scenic views etc.)
Examples are: banking services, hotel services,
Marketing Myopia: Focusing more on product than providing experience and services produced by these products.
These sellers will face difficulty if new competitor enters and provide superior customer services. Customers will definitely switch to competitors.
For example: Walt Disney make you feel as if you really in wonder world.
Example: American girl provide its customers not only just dolls but pleasant experiences and services in its stores.
Customer value and satisfaction:
To fulfil the needs of customers there are number of market offerings, and customer will choose the product which will satisfy and value his expectations.
Customers can easily switch to competitors if they provide them high value and satisfaction.
So, customer value and customer satisfaction are key building blocks for developing and managing customer relationships.
Exchanges and relationships:
Exchange: is the act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return.
In other words, marketers try to get some positive response in return of marketing offerings.
Examples: church want membership, social action group wants idea acceptance.
Marketing is actions taken to create, maintain and grow desirable exchange relationships by involving a product, service or idea or any other object.
Companies want to build strong relationships by consistently providing superior customer value.
Markets:
Market is a set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service.
Buyers often share particular needs and wants that can be satisfied through exchange relationships.
Marketing means managing markets to bring about profitable exchange relationships.
Sellers should search for customers, identify their needs, design good market offering, set prices for them and store and deliver them.
Marketing activities involved are consumer research, product development, communication, distribution, pricing and services.
Buyers also adopt marketing strategies.
In today’ world, especially through digital means made marketing two-way affair.
So, marketers should effectively deal with customer-managed relationships.
Marketing today is not only just asking, how we can influence customers but how customers can influence us or how customers can influence each other.
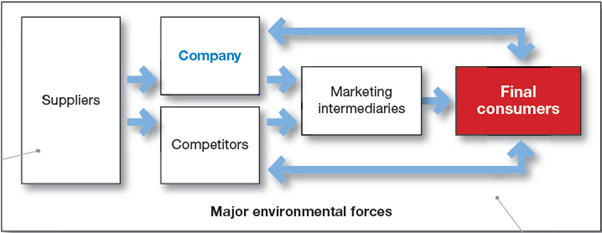
Major environmental forces (demographic, economic, natural, technological, political and social) greatly effect each party.
Each party in the system add value for the next level.
Profitable relationships not only just depend upon how well one party played but how well the entire system serve the final consumer’ need.
Customer Value-Driven Marketing Strategy:
The aim of marketing manager is to engage, keep and grow target customers by creating, delivering and communicating superior customer value.
To design a winning marketing strategy requires managers to answer two important questions. First is, which customers will we serve and second how to serve them best (what is value proposition).
Selecting Customers to Serve:
Companies need to decide, who will be their customers, who will they serve. Companies do it by dividing them into segments (market segments) and then selecting which market to target (target marketing).
Selecting all the customers is not a good idea, because marketing managers know well that they cannot serve all customers with different demands. And in serving all customers, companies fail to provide satisfactory services to any customer.
Choose a Value Proposition:
Value proposition is the set of benefits and values, company promises to deliver to customers to satisfy their needs. How it will differentiate and position itself in the marketplace.
Example: As Spirit Airlines says: “Less money, more Go”
Marketing Management Orientation:
Marketing managers always want to engage their targeted customers and build a profitable relationship with them, the question is how? there are following five concepts through which organizations design and carry out marketing strategies.
· The Production Concept: This concept guide sellers that, consumers will buy products which are highly affordable and available in the market. So, management should focus on how to improve production along with efficient distribution.
This concept leads to Marketing Myopia (Myopia, is nearsightedness), in this concept organizations focus on just making products available in the market rather than customer satisfaction, product utility etc.
· The Product Concept: Product concept says that, consumers will weigh products due to its quality, performance and innovative features. With this concept, marketing strategies focus on bringing improvements in the product. This also leads to marketing myopia, as companies put all their energies on product development and ignoring other customer related factors.
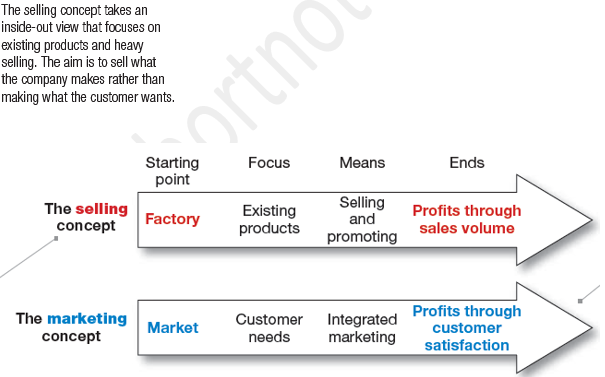
· The Selling Concept: This concept, companies need to put maximum efforts on large-scale marketing and sales techniques. This technique is used for the products, which customers often don’t buy. In the selling concept, companies focus on maximizing sales transactions rather than building long-term relationship with customers. This is inside-out perspective.
· The Marketing Concept: It is customer centric concept; it revolves around satisfying customer needs and wants. Its not about finding the right customer for your product, but finding the right product for your customers. Customer driven companies research customers to understand their needs, their desires, gather new ideas, and test product improvements. This is outside-inn perspective, these strategies work well when customers know what they want, and a clear need exists. Customer-driven strategies even help in understanding customer needs when they don’t know about, what they want, and about their needs.

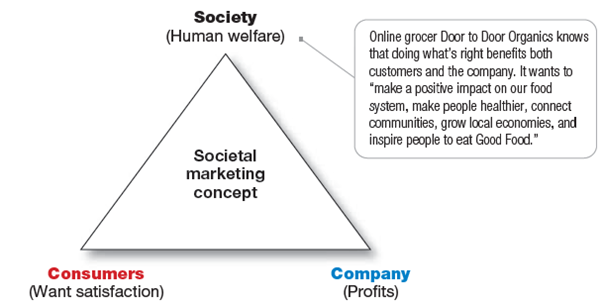
· The Societal Marketing Concept: It says marketing strategies should meet consumer needs and wants along with this; these strategies should have long-term impact for the betterment of society. Now companies have started focusing on their economic growth as well as customers well-being.
Sustainable marketing: societal marketing includes the concept of sustainable marketing, that is, meeting the needs of both consumers and businesses, and along with this, enhancing or preserving the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
Shared Value: It focusses on creating economic value in a way that also creates value for society.
One renowned marketer named this societal marketing concept as Marketing 3.0.
Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program:
Marketing strategy highlights who will be their customers and how to create value for them. second, marketers develop a marketing program which will actually deliver the said value to the customers.
This marketing program strengthens relationship with customers by transforming the marketing strategy into action. It includes Marketing mix, the Four Ps. i.e., Product, Price, Place and Promotion.
· Product: what are the offerings of organization for customers
· Price: how much will it cost to customers
· Place: who will be the target consumers.
· Promotion: how to communicate let customer know about organization’ products or offerings.
Marketers should use blend of these four Ps or Marketing Mix develop an integrated marketing program in order to engage customers and to deliver the intended value to customers.
Engaging Customers and Managing Customer Relationships:
In this topic we will see customer relationship management and how to engage customers to deeper level in this age of digital and social marketing.
Customer Relationship Management:
This is the most modern concept of marketing. Customer relationship management is delivering superior value and satisfaction to customers, and building and maintaining profitable customer relationship. It deals with all aspects of acquiring, engaging and growing customers.
Relationship Building Blocks: Customer Value and Satisfaction, satisfied customers are more loyal customers. To make customers satisfied, it is important to provide them superior customer value. When a customer thinks to buy a product, he will find number of products to satisfy his need, but he will choose only which will offer highest Customer-Perceived Value. This value can vary from customer to customer, some customer may value the price of product, other customers may value the quality of product.
Customer Satisfaction: “It is the product’ perceived performance relative to buyer’ expectations.”
· If performance is less than expectations, customer is dissatisfied.
· If product performance matches the expectations, then the customer is satisfied.
· And if product performance exceeds expectation, then customer is highly satisfied or delighted.
Companies promise customers what they can deliver, and deliver more than they promised and customer’ expectations. This makes customer highly satisfied and loyal to company. Such highly satisfied customers make repeat purchase and often become marketing partners, by providing information to their peers, friends, colleagues family etc. As a result, company will achieve the goal of making profit.
Customer Relationship Levels and Tools: Organizations can build relationships with customers at different levels, it depends upon the target market. There are following two extremes,
· First is, offering quality products or services on very cheaper rates in the market, in this companies cannot call each and every customer to build relationship. Quality of product and its price will make it dominant and improve the brand image, Example is P&G’ (Pampers diapers, Ariel surf, Pantene shampoo) Products are almost the basic necessities of so many houses.
· Second, sales staff of P&G build relationship with mega stores, Cash n Carry’s, Walmart etc. who sell their products by displaying on the front.
· Frequency marketing Programs: It is to build relationships with customers by rewarding them for their repeat purchases.
Customer Engagement and Today’ Digital and Social Media:
Customer engagement is different from old marketing i.e., selling products to consumers. Its goal is to make the product an important part of consumer’ lives and conversations to shape brand conversations, experiences and community.
Earlier, companies used to focus on mass marketing to broad segments of customers at arm’ length. But today’ fast growing internet and social media has enabled companies to customer-engagement marketing.
Today, consumers are more informative, this leads marketers to put their serious focus on Customer-Managed Relationships. In this customer are in contact with companies, and help each other to make better brand experience.
Companies now do marketing through Attraction rather than by Intruding. They attract customers by combining mass-media with the mix of social media, mobile and online marketing that promotes consumer engagement, brand advocacy and brand conversation among customers.
Consumer-Generated Marketing:
In this type of marketing, consumers play their role in shaping their brand experience and of others. Consumers do it through video sharing sites, social media, blogs and other digital forums. Companies also take special measures and invite customers to play active role in shaping products and brands.
Example: Airbus set the seat size of its then launched A330neo, as per passengers’ opinions shared on social media.
Partner Relationship management:
Marketers have now realized that, in this world full of connections, along with customer relationship management, Partnership Relationship Management is also very important.
It is important to keep strong bond with internal and external partners. Each and every functional can now interact with customers to know about their needs and preferences. It is also important to keep strong relationship with distributors and retailers as they act as bridge to connect them with customers. Then efficient Supply Chain Management includes to keep good relations with suppliers and components to final product and that are carried to final buyers.
All these factors combine to bring more value to customers.
Capturing Value from Customers:
This is the final step in marketing process, capturing value from customer is in the form of sales, market share and profits. When companies provide superior customer value, customers become loyal which in turn means greater long-run returns for the company.
Creating Customer Loyalty and Retention:
When company is good at customer relationship management, it creates satisfied customers, in result these satisfied customers become loyal to company and talk favorably with others about the company and its products.
Research suggests that it five times cheaper to keep an old customer than acquiring new one. Losing a customer means losing the entire stream of purchase that the customer throughout the life. This the Customer Lifetime Value.
Examples: (i) Lexus, has estimated that a single satisfied customer worth more than $600,000 in lifetime sales. (ii) estimated lifetime value of Starbucks customer is more than $14,000.
Growing Share of Customer:
Good customer relationship management helps marketers to increase their share of customer. It is the share of customer’ purchasing in the relevant product category. To increase the customer share, companies can offer variety, discounts, greater value to its current customers.
Examples: banks want to increase “share of wallet”, airlines want to increase “Share of travel”
Building Customer Equity:
It is the combined customer lifetime values of all of company’s customers. Market share and sales shows the past and customer equity suggests the future. The more loyal customer a company have, the higher its customer equity.
Building Right Relationships with Right Customers: companies should carefully handle customer equity. Loyal customers should be treated as assets of company that needs to be managed and maximized. Not all loyal customers are profitable and surprisingly some disloyal customers can be profitable.
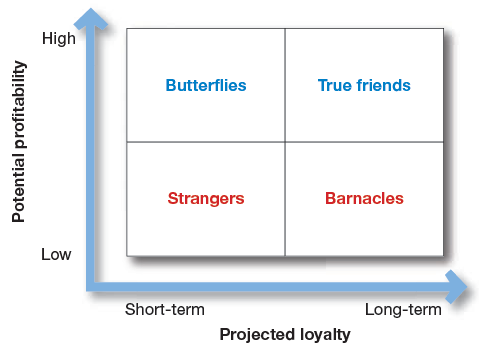
In the above mention figure, four relationship groups are classified. Which are briefly described below.
· Strangers: Strangers are very little loyal and show very low profitability potential. There is very little fit between their needs and company’ offerings. Company’ strategy should be very simple, that don’t invest in such customers and make money on each transaction.
· Butterflies: this type of customers are not loyal but are potentially profitable. There is a good fit between customers needs and company’ offerings. Efforts to make these customers are often unsuccessful. So, companies try to capture as much as more profit in short period of time.
Example; Stock market investors.
· True Friends: These are both profitable and loyal. There is strong fit between customer’s needs and company’ offerings. Companies need to invest in these customers to engage, nurture and grow them. companies try to turn them into True Believers who do repeat purchases and tell others about their good experience.
· Barnacles: Barnacles are highly loyal but very less profitable. There is a limited fit between the needs of customers and company offerings. Companies can increase their profitability by selling them more and if still they are not profitable, companies can fire them.
Example; smaller customer of bank, who have account in the bank from so long, the account is so small that bank don’t get any profit out of it.
Conclusion: customers of different relationship groups require different engagements and relationship management strategies. And aim is to build the right relationships with right customers.
Change have become part of daily life. Richard Love of HP said “the pace of change is so rapid that the ability to change has now become a competitive advantage.”
There are five major developments which are changing the marketing landscape and challenging marketing strategy are; (i) The digital age, (ii) Changing economic environment, (iii) The growth of not-for-profit marketing, (iv) Rapid globalization and (v) The call for sustainable marketing practices. Let’s briefly discuss each.
The Digital Age: Online, Mobile, and Social Media Marketing:
This the age of Internet of Things (IoT), an environment, where everyone and everything is digitally connecting to everyone and everything else. The dramatic growth in digital technology has changed the way we live, how we communicate, how to share information, shop and access entertainment.
Digital and social media marketing involves using different digital media marketing tools such as, mobile adds, social media, websites, emails, blogs, mobile apps and other digital platforms to engage consumers anytime, anywhere through their tablets, smartphones, computers and other digital devices.
Social Media Marketing:
In today’ digital world, almost every brand website or a traditional media is linked with social world i.e., Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Instagram, and other social media sites. Because social media enable companies to engage customers in exciting ways, and get people speaking about them.
Social media is a kind of digital home for so many people, as people use to spend time there, get entertained and share information. so, it provides an ideal platform to marketers for Real-time Marketing, through which marketers can engage customers by linking them with important trending topics, causes, real-world events or other important happenings from consumers lives.
Example: NASA have more than 480 social media accounts, spanning different topics. Through which they engage customers.
Mobile Marketing:
This is an ideal platform form marketers to engage customers as mobile phones are ever present, finely targeted, always on and highly personal. Every four out of five smartphone users use their phones to search for a product, doing price comparisons, reading product reviews, finding and redeeming coupons etc. purchases from mobile phones is made immediate, enrich brand experience and make shopping easier.
Example: KFC’ customers can find the nearest outlet, about their products and pricing.
The Changing Economic Environment:
If we talk about today (2021-2022), inflation is at it’s peak if we compare it with past. Earlier people use to overspend buy unnecessary products etc. but now, during high inflation, consumers are bringing back their spendings in line with their incomes and rethink their buying priorities.
Now in this era, people are reconsidering the definition of good life. People have started doing things just more sensibly. One consumer gave his opinion “we are moving from mindless to mindful consumption.”
In times of trouble, companies use to cut marketing cost, but one thing should be kept in mind that, making cuts in wrong places can damage long-term brand image and customer relationship.
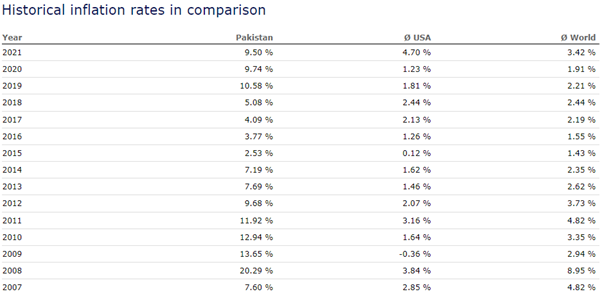
Below mentioned is the 15 years historical data comparison between, Pakistan, USA and the World.
The Growth for Not-for-Profit Marketing:
In recent times, marketing has also become vital for
not-for-profit organizations. Because now they face so much competition in the
market for support, funds and memberships, so they need to engage people, show
them what is their cause, involve them, so they become members of organization.
Example: Shaukat Khanum Memorial hospital, it’s a charity
hospital for cancer patients. We often see their marketing campaigns for fund
raising on TVs, billboards etc.
Rapid Globalization:
Global competition has affected almost every company
whether its large or small. Manager need to learn how local marketing is
different from global marketing. How to compete in the world which has now
become a global village.
Examples:
Apple US based organization has set-up a plant in China.
McDonald’s (US based) is serving around 70 million customers in
36000 local restaurants and 100 countries world-wide, more than 68% of its sale
comes from outside the United States.
Toyota (HQ in Japan), Nestle (HQ in Switzerland),
Samsung (HQ in South-Korea) often outperforms US based competitors in the American
markets.
Sustainable Marketing-The call for More Environmental
and Social Responsibility:
Sustainable marketing is to consider social values and
responsibilities as important. Customers today demands companies to do good to
the society and be environment friendly. Some companies ignore this basic need
for them to grow in future, they only do good when legislative pressure is
built. But there are so many companies who have understand this call of society
and take part in the betterment of society and environment.
Example:
Coca Cola, they focus on waste management and
preservation of water.
Sukh Chain builders (Pakistan) they maintain a family
park in Islamabad which include facilities like jogging track, exercise arena,
sports arena, drinking water, washrooms etc.